Investing in stocks remains one of the most popular and effective strategies for building long-term wealth, and choosing the right stocks can make all the difference. Among the various categories of stocks available, blue chip stocks are widely regarded as some of the safest and most dependable. These companies are recognized for their financial strength, consistent performance, and resilience during economic downturns. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about blue chip stocks what they are, how to evaluate them, their benefits, and answers to frequently asked questions.
Key Takeaways
What Are Blue Chip Stocks?
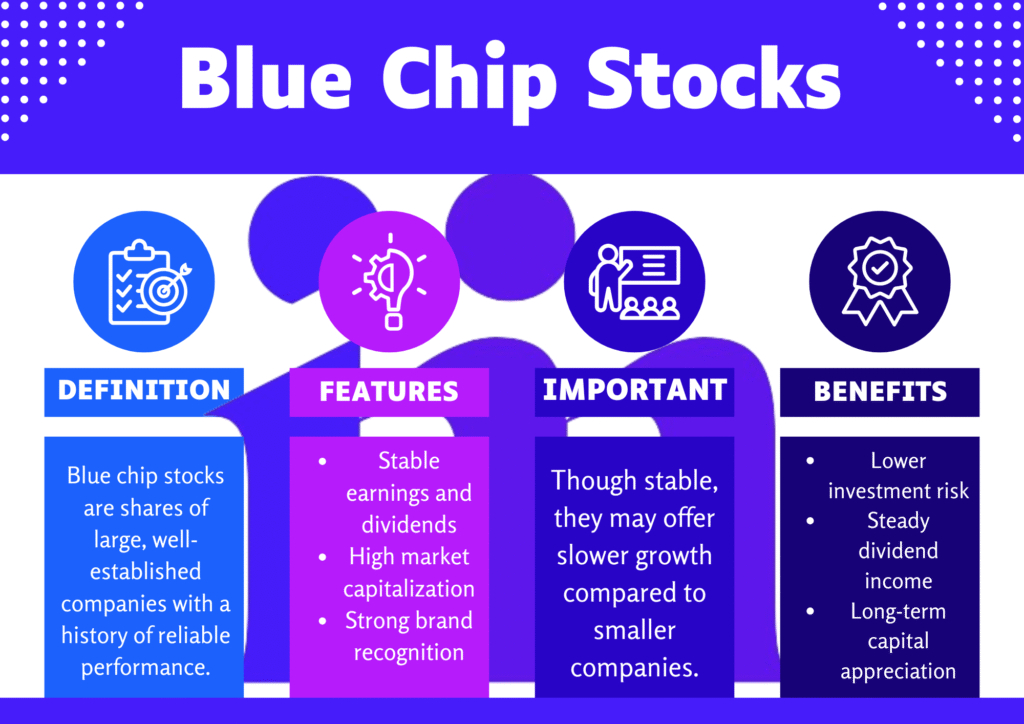
Blue chip stocks are securities of well-established, financially stable companies with a pathway record of trustworthy accomplishment and strong market capitalization. The term “blue chip” comes from poker, where blue chips hold the highest value similarly, these stocks are valued for their reliability and ability to generate profits even in challenging economic conditions.
These companies are often industry leaders and known for delivering consistent revenues and profits, typically returning a portion to shareholders through dividends. Blue chip stocks usually fall under the large-cap category (with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more) and operate across sectors such as technology, healthcare, finance, consumer goods, and energy.
Blue chip stocks are not a substitute for a diversified portfolio. Even though they’re known for stability and steady dividends, relying solely on blue chips can expose you to sector-specific or market-wide risks. Always aim for diversification across industries and asset classes to better protect your capital.
Characteristics of Blue Chip Stocks
To be considered a blue chip stock, a company generally exhibits the following features:
- Robust Financial Performance
Blue chip companies consistently post strong earnings, stable revenue growth, and high profit margins. Their financial statements show resilience across market cycles. - Industry Leadership
These firms command leading market positions with strong brand recognition and sustainable competitive advantages. - Regular Dividend Payments
Most blue chip corporations pay stable dividends, usually on a three-monthly or annual basis, replicating their financial power and shareholder assurance. - Stability and Longevity
Blue chip firms have often been operating for decades and have demonstrated their ability to navigate recessions, market corrections, and industry disruptions. - Lower Volatility
These stocks generally exhibit less price fluctuation than small or mid-cap stocks, making them more attractive to risk-averse investors. - Effective Corporate Governance
Blue chip companies are typically well-managed, with transparent governance structures and experienced leadership.
Reinvest dividends to maximize compounding. Use a Dividend Reinvestment Plan (DRIP) or manually reinvest your blue chip stock dividends to buy more shares. Over the long run, this strategy can significantly accelerate your portfolio’s growth thanks to the power of compounding.
How to Select Blue Chip Stocks
Investing in blue chip stocks can be a clever long-term approach, but suspicious collection is key. Here are the most important conditions to count:
- Analyze Financial Strength
Look for companies with strong balance sheets, low debt-to-equity ratios, high operating margins, and solid cash flows. These indicators reflect a company’s ability to sustain profitability and weather downturns. - Review Dividend History
Assess whether the corporation has a reliable track profile of repaying and growing dividends. A stable or increasing dividend is a durable sign of financial steadiness. - Evaluate Market Leadership
Choose firms with dominant market positions, consistent innovation, brand strength, and customer loyalty. These factors contribute to long-term sustainability. - Examine Earnings Growth
Look for companies with consistent earnings-per-share (EPS) growth. This indicates adaptability and ongoing value creation. - Assess Valuation
Use metrics like the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios to determine if a stock is reasonably priced. Even blue chips can become overvalued during bullish markets. - Consider Economic Moats
An economic moat denotes a corporation’s long-term economical edge. Blue chip stocks often enjoy durable advantages such as proprietary technology, brand equity, or network effects. - Check Market Capitalization
Blue chip stocks characteristically fall into the large-cap classification ($10B+). Their size and resource depth often translate to greater stability and less market sensitivity.
Some blue chip companies like Coca-Cola and Procter & Gamble have paid dividends for over 50 consecutive years. This consistency highlights their financial resilience and commitment to shareholders even through recessions, wars, and market crashes.
Pros and Cons of Blue Chip Stocks
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✔ Lower volatility and dependable returns | ✘ Not ideal for short-term speculative investors |
| ✔ Consistent dividend payouts for income | ✘ Still subject to systemic market risks |
| ✔ Strong performance during downturns | ✘ May be overvalued during certain market phases |
| ✔ Industry leadership and brand stability | ✘ Limited high-growth potential compared to smaller, riskier stocks |
As someone who has tracked dividend-paying blue chip stocks for over a decade, I’ve learned that patience is your biggest asset. These aren’t the flashiest investments, but they often provide peace of mind, especially during volatile markets. When your portfolio keeps generating income even when prices fall that’s when you truly appreciate the value of blue chips.
Advantages of Investing in Blue Chip Stocks
- Stability and Reliability
These companies offer dependable performance across market cycles, making them ideal for conservative investors. - Dividend Income
Regular dividend payments provide a steady income stream, which can be reinvested or used as passive income. - Lower Risk Exposure
Compared to speculative or small-cap stocks, blue chips offer reduced volatility and greater financial stability. - Long-Term Growth
While not explosive in growth, blue chip companies deliver steady appreciation through innovation, acquisitions, and expanding market share. - Portfolio Diversification
Blue chip stocks span various sectors, allowing investors to diversify and reduce overall portfolio risk.
During the 2008 financial crisis, Johnson & Johnson’s stock price dipped but the company never cut its dividend. While many companies suspended payouts, J&J maintained its dividend growth streak, showing why blue chip investors value long-term reliability over short-term gains.
10 Examples of Blue Chip Stocks
Here are 10 widely recognized blue chip stocks with proven track records:
- Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Sector: Technology
An international leader in end user electronics with durable salaries and dividend evolution. - Microsoft Corporation (MSFT)
Sector: Technology
A key player in software and cloud computing with consistent long-term growth. - Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
Sector: Healthcare
Known for its diversified product line and long-standing dividend reliability. - Procter & Gamble Co. (PG)
Sector: Consumer Staples
A household name with stable cash flows and a commitment to dividend increases. - Coca-Cola Company (KO)
Sector: Consumer Staples
A global beverage giant with a long dividend history and brand dominance. - Visa Inc. (V)
Sector: Financial Services
A payment handling leader with great sidelines and steady growth. - Walmart Inc. (WMT)
Sector: Retail
The largest retailer in the world with resilient earnings and dividend growth. - McDonald’s Corporation (MCD)
Sector: Consumer Discretionary
A global fast-food chain with reliable cash flows and international expansion. - Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (BRK.B)
Sector: Conglomerate
Led by Warren Buffett, it holds a diverse portfolio of high-performing assets. - PepsiCo Inc. (PEP)
Sector: Consumer Staples
A leader in food and beverage with strong brand equity and reliable dividends.
Not all big companies are true blue chips. Some large-cap stocks may appear stable but lack the consistent earnings, strong balance sheet, or dividend history that define true blue chips. Always research a company’s fundamentals before assuming it qualifies.
Conclusion
Blue chip stocks represent some of the most dependable and resilient investments in the market. With a combination of stability, regular dividend income, and solid long-term growth potential, they are well-suited for both novice and seasoned investors. By focusing on financial health, market dominance, and fair valuation, you can build a diversified portfolio of blue chip stocks that delivers consistent returns and long-term wealth accumulation.
Whether you’re planning for retirement or seeking steady portfolio growth, blue chip stocks remain a cornerstone of sound, low-risk investing.






