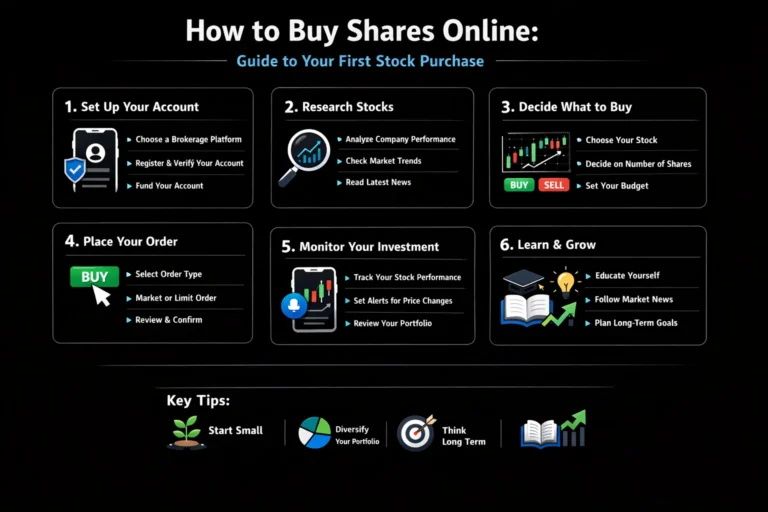
10 Best Ways to Invest Money for Long-Term Financial Success
Taking control of your financial future starts with the right investment strategy. This guide cuts through the noise to review the most effective ways to grow your wealth over the long term. We help you find the perfect fit for your goals and risk tolerance, whether you’re in the US, UK, or Canada, to build wealth and achieve financial freedom.
What are Long-Term Investments
Long-term investing is the practice of holding assets for many years, or even decades, to capitalize on compound growth and weather short-term market volatility. Unlike day trading, it’s not about timing the market but about time in the market. The core principle is to buy and hold quality assets that are expected to appreciate in value over an extended period, allowing your money to work for you and build substantial wealth for goals like retirement, financial independence, or leaving a legacy.
Key Takeaways
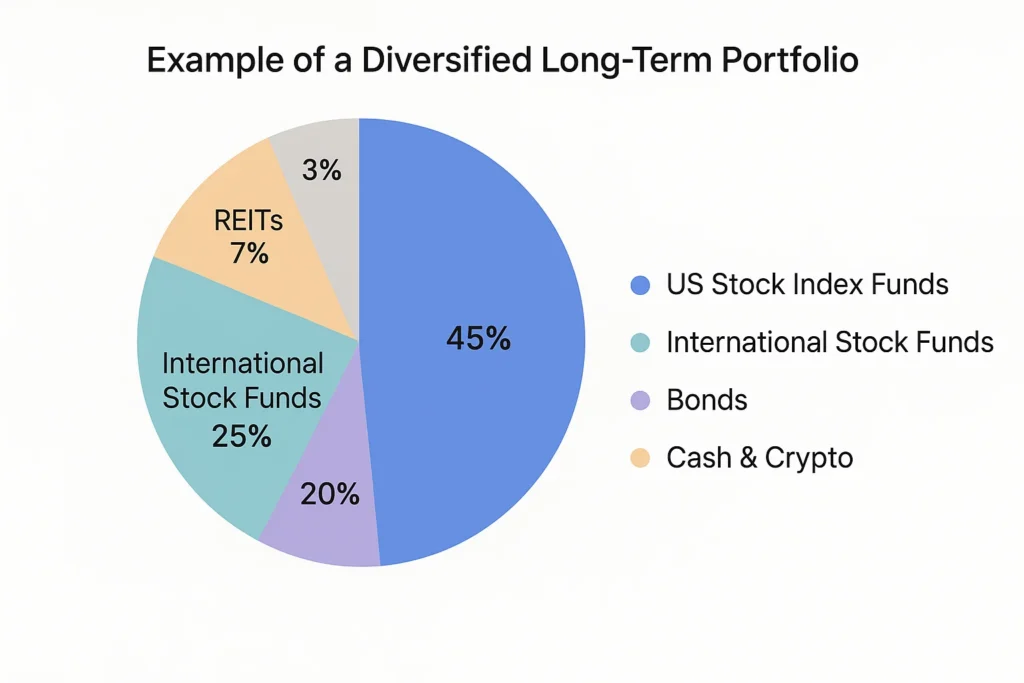
Goal-Based Investment Selection
| Your Primary Goal | Best Investment Type | Key Feature & Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Core Wealth Building | Stock Market Index Funds/ETFs | Broad diversification, low fees, and historical long-term growth. |
| Retirement Savings | Tax-Advantaged Accounts (IRA, 401(k), ISA) | Tax-free growth or deductions, automating retirement savings. |
| Capital Preservation & Income | Bonds & Fixed Income | Lower volatility than stocks and provides regular interest payments. |
| Diversification & Inflation Hedge | Real Estate (via REITs) | Provides exposure to property markets without the hassle of direct ownership. |
| High-Risk Growth | Growth Stocks & Sector Funds | Potential for higher returns, but comes with significantly higher volatility and risk. |
For investors in the UK, utilizing a Stocks and Shares ISA is crucial for tax-free growth, while US investors should prioritize maxing out their 401(k) employer match and IRA contributions first. Always check the local tax wrappers available to you.
Our Top 10 Long-Term Investment Picks
We’ve analyzed the most effective and time-tested strategies for building long-term wealth. Here are our top 10 picks for 2025, broken down by their strengths, ideal investor profile, and how they fit into a diversified portfolio.
1. Stock Market Index Funds (S&P 500, FTSE All-Share)
Overall Score: 5/5
Best For: The core of nearly every long-term portfolio; hands-off investors.
Pricing: Very low (Expense Ratios typically 0.03% – 0.20%)
An index fund is a type of mutual fund or ETF designed to track the performance of a specific market index, like the S&P 500 or the FTSE All-Share. It offers instant diversification across hundreds of companies.
Key Features:
- Instant Diversification
- Extremely Low Fees (Expense Ratios)
- Passive Management
- Strong Historical Long-Term Returns
- High Liquidity
- Simplifies investing; you buy the entire market.
- Low costs mean more of your money compounds.
- Consistently outperforms the majority of actively managed funds over the long run.
- You will never beat the market; you will only match its returns (minus fees).
- Fully exposed to overall market downturns.
Why We Picked It: We chose Index Funds for the #1 spot because they are the most reliable, cost-effective, and accessible way for the vast majority of people to build wealth in the stock market. They are the foundational building block of a sound long-term strategy.
2. Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans (401(k), Workplace Pension)
Overall Score: 5/5
Best For: Anyone with access to one, especially with an employer match.
Pricing: Varies; often includes low-cost fund options and significant tax advantages.
These are tax-advantaged accounts set up by your employer. In the US, this is a 401(k); in the UK, it’s a workplace pension. Contributions are often automatically deducted from your salary.
Key Features:
- Tax Deferral (Traditional) or Tax-Free Growth (Roth)
- Employer Matching Contributions (essentially free money)
- Automated Payroll Deductions
- High Contribution Limits
- An employer match provides an immediate, guaranteed return on your investment.
- Automation makes saving effortless and consistent.
- Reduces your taxable income (for traditional plans).
- Limited investment choices determined by the plan provider.
- Withdrawal restrictions before retirement age.
Why We Picked It: It’s the closest thing to a sure thing in investing. Failing to contribute enough to get your full employer match is like turning down a pay raise.
3. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Overall Score: 4/5
Best For: Adding real estate exposure without being a landlord; earning dividend income.
Pricing: Varies; traded like stocks with associated brokerage fees.
REITs are corporations that own, work, or finance income-producing real estate. They allow you to invest in a portfolio of properties (e.g., apartments, malls, offices) by buying shares.
Key Features:
- High Dividend Yields (required by law to pay out 90% of taxable income)
- Portfolio Diversification
- High Liquidity (compared to physical property)
- Inflation Hedge
- No need for a large capital outlay or to deal with tenants and toilets.
- Provides a source of passive income.
- Low correlation with stocks, providing diversification benefits.
- Can be sensitive to interest rate hikes.
- Dividend income is usually taxed as conventional revenue.
Why We Picked It: REITs democratize real estate investing, making a powerful wealth-building asset class accessible to everyone with a brokerage account.
4. Roth IRA (US) / Stocks and Shares ISA (UK)
Overall Score: 5/5
Best For: Tax-free growth and withdrawals in a self-directed account.
Pricing: Varies; account itself is free, but you pay for the investments you hold within it.
These are not investments themselves, but powerful tax-advantaged wrappers or accounts. In the US, the Roth IRA allows for after-tax contributions and tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement. In the UK, a Stocks and Shares ISA allows you to invest without paying any tax on capital gains or dividends.
Key Features:
- Tax-Free Growth and Withdrawals
- Wide Choice of Investments (Funds, Stocks, ETFs, Bonds)
- Annual Contribution Limits (e.g., $7,000 for US IRA in 2024, £20,000 for UK ISA)
- Flexibility and Control
- The ultimate tool for tax-efficient investing; all your profits are yours to keep.
- Provides flexibility to choose your own investments.
- Withdrawal rules (especially for Roth ISA/Roth IRA) are flexible for certain life events.
- Annual contribution limits cap how much you can invest tax-free each year.
- Requires you to be proactive in selecting and managing your investments.
Why We Picked It: For anyone looking to build wealth outside of an employer plan, these accounts are non-negotiable. They provide a massive advantage by shielding your compounding returns from taxes.
5. Individual Stocks
Overall Score: 3/5
Best For: Experienced investors willing to do deep, ongoing research.
Pricing: Brokerage trading commissions (many are now $0), plus the risk of capital loss.
Buying individual stocks means purchasing shares of ownership in a specific public company (e.g., Apple, Tesla, Amazon). This offers higher potential returns than a fund but comes with significantly higher risk.
Key Features:
- Direct Ownership in a Company
- Potential for Outsized Returns
- Voting Rights (on company decisions)
- Requires Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Unlocked potential for returns that far outpace the broader market.
- Allows you to bet directly on companies and sectors you believe in.
- High risk; a single company can go bankrupt, resulting in a 100% loss.
- Requires substantial time, research, and emotional discipline.
- It is very difficult to consistently beat the market over the long term.
Why We Picked It: We include it because it’s a well-known path, but with a cautious rating. For most, it should only be a small satellite portion of a portfolio that is anchored by diversified index funds.
6. Bonds & Fixed Income
Overall Score: 4/5
Best For: Capital preservation, generating income, and reducing portfolio volatility.
Pricing: Varies; you can buy individual bonds or bond funds (ETFs) for low fees.
When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending money to a government or corporation for a fixed period in return for regular interest payments. Upon maturity, you get your initial investment back.
Key Features:
- Regular Interest Payments (Coupons)
- Lower Volatility Than Stocks
- Capital Preservation (if held to maturity)
- Inverse Relationship to Interest Rates
- Provides stability and ballast to a portfolio, smoothing out returns during stock market downturns.
- A reliable source of passive income.
- Generally considered a safer asset class than stocks.
- Returns are typically much lower than stocks over the long run.
- Vulnerable to inflation risk (inflation can outpace bond returns).
- When interest rates increase, the market value of current bonds decreases.
Why We Picked It: Bonds are a critical component of a diversified portfolio, especially as you get closer to your financial goal and cannot afford a major market crash.
7. Cryptocurrency & Digital Assets
Overall Score: 2/5
Best For: A high-risk, speculative satellite allocation for those who can afford to lose their entire investment.
Pricing: Highly volatile; plus potential exchange and network fees.
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security, operating on decentralized networks called blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). They are a highly speculative asset class.
Key Features:
- Extreme Volatility
- Decentralization (No central bank or government control)
- 24/7 Market
- Emerging Technology (Blockchain)
- Potential for astronomical returns.
- Offers diversification from traditional financial systems.
- Groundbreaking underlying technology with long-term potential.
- Extreme risk of total and sudden loss of capital.
- Regulatory uncertainty.
- No intrinsic value; price is driven purely by supply and demand sentiment.
Why We Picked It: We include it to acknowledge its role in modern portfolios but with a strong warning. It should only ever constitute a very small portion of capital you are fully prepared to lose.
8. Robo-Advisors
Overall Score: 4/5
Best For: Completely hands-off, automated portfolio management for beginners.
Pricing: Low (typically 0.25% – 0.50% annual management fee on top of fund fees).
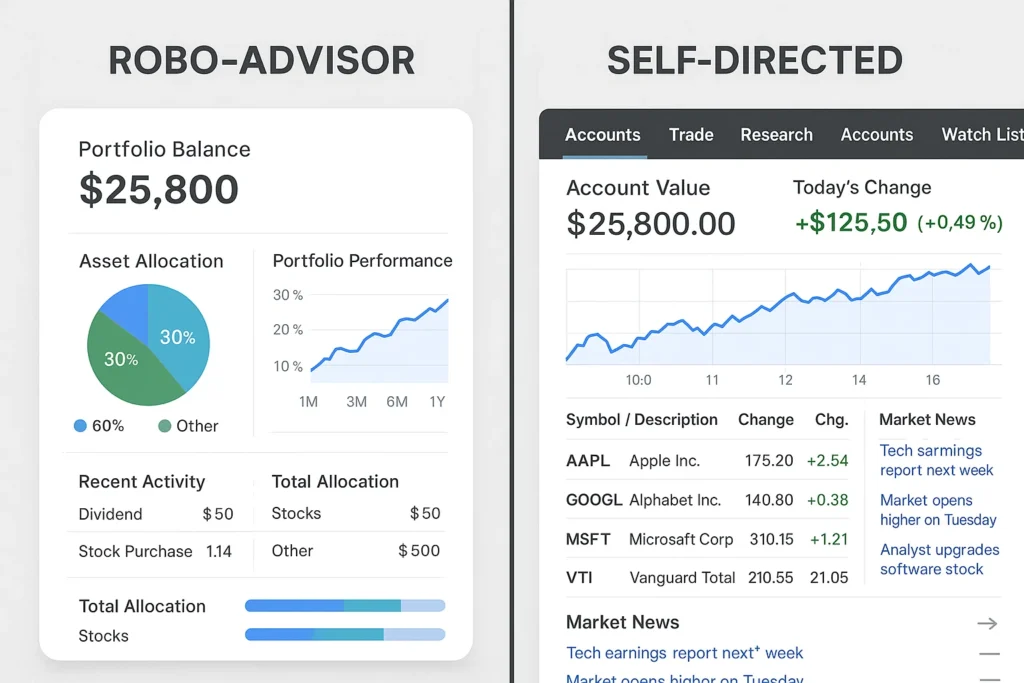
Robo-advisors are digital platforms that provide automated, algorithm-driven financial planning and investment services with minimal human supervision. They build and manage a diversified ETF portfolio for you based on a questionnaire.
Key Features:
- Automated Portfolio Management
- Low Minimum Investments
- Automatic Rebalancing
- Tax-Loss Harvesting (on some platforms)
- The ultimate in simplicity; set it up once and it runs itself.
- Provides professional-grade diversification and management at a low cost.
- Removes emotion from the investing process.
- You have little to no control over the specific assets in your portfolio.
- The management fee, while low, is an additional cost over a pure DIY index fund approach.
Why We Picked It: Robo-advisors are a fantastic innovation that makes sophisticated, hands-off investing accessible to the masses at a reasonable price.
9. Dividend Growth Stocks
Overall Score: 4/5
Best For: Investors seeking a growing stream of passive income and lower volatility.
Pricing: Brokerage commissions; focus is on company quality, not just price.
This strategy involves investing in well-established, profitable companies with a history of consistently increasing their dividend payments to shareholders year after year (e.g., Johnson & Johnson, Procter & Gamble).
Key Features:
- Growing Passive Income Stream
- Focus on Mature, Stable Companies
- Potential for Total Return (Income + Growth)
- Lower Volatility Than Non-Dividend Stocks
- Provides a tangible, growing income, which is powerful in retirement.
- Dividend-paying companies are often financially stable and high-quality.
- Reinvesting dividends supercharges compounding.
- Not immune to market downturns.
- Companies can cut dividends during severe economic crises.
- Can underperform high-growth, non-dividend stocks during bull markets.
Why We Picked It: It’s a time-tested strategy for building wealth and income simultaneously, appealing to those who value seeing cash returns in their account.
10. Your Own Education & Skills
Overall Score: 5/5
Best For: Everyone. It’s the foundation upon which all other investments are built.
Pricing: Varies (courses, books, time investment).
This is the most overlooked but highest-returning investment you can ever make. Increasing your knowledge and skills directly increases your earning potential, which in turn increases the amount of capital you have available to invest.
Key Features:
- Directly Increases Earning Power
- Improves Financial Literacy
- Builds Career Security
- Compoundable Knowledge
- The returns are not tied to market performance.
- It can never be taken away from you.
- A higher salary provides more capital to invest and a larger safety net.
- Requires an upfront investment of time, effort, and sometimes money.
- The returns are not as immediately quantifiable as a stock price.
Why We Picked It: We bookend the list with this because it is the ultimate wealth-building tool. A high-income earner who invests poorly will still likely outperform a low-income earner who invests perfectly. Your human capital is your most valuable asset.
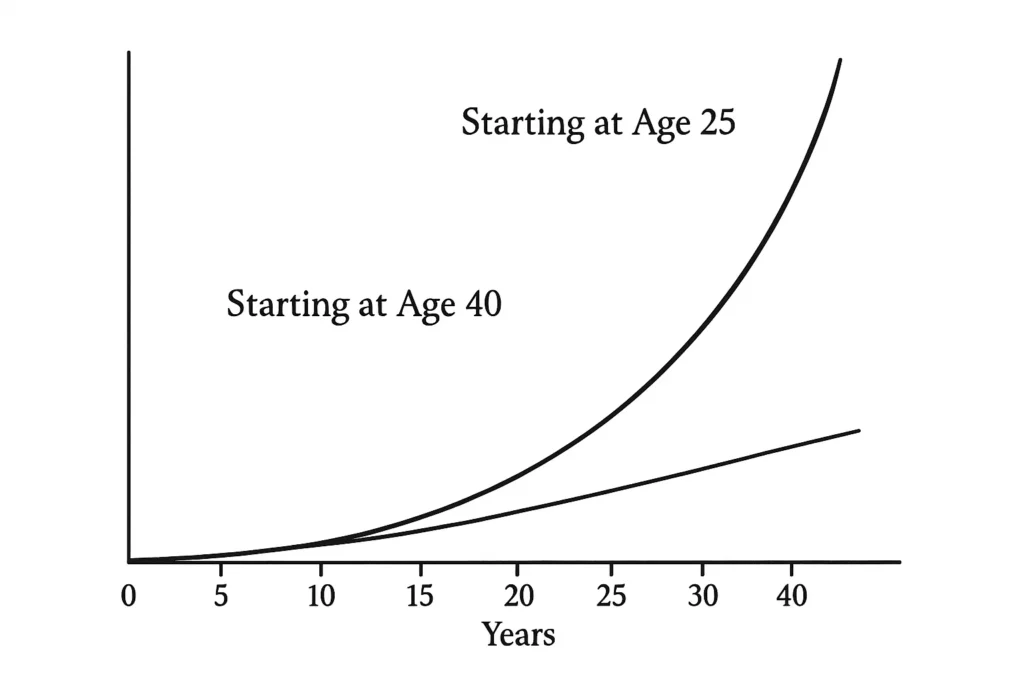
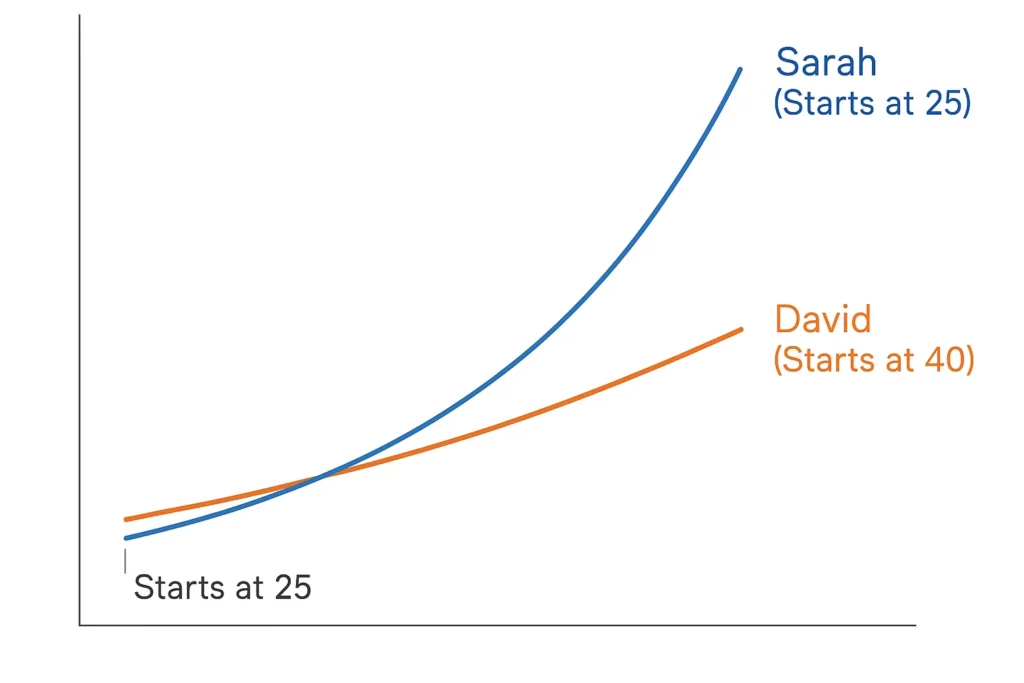
A Real-World Example: The Power of Starting Early
Consider Sarah, a 25-year-old graphic designer in the US who starts investing $300 a month into a low-cost S&P 500 index fund within her Roth IRA. Assuming a conservative 7% annual average return, she would contribute $144,000 over 40 years. However, thanks to compound interest, her portfolio would grow to approximately $720,000 by age 65.
Now, consider David, a 40-year-old teacher in London who realizes he needs to catch up. He starts investing $600 a month into a global index fund within his Stocks and Shares ISA. After 25 years with the same 7% return, he will have contributed $180,000, but his portfolio would be worth approximately $473,000. Sarah’s extra 15 years of compounding made a dramatic difference, highlighting the power of starting early.
Long-Term Investing vs Day Trading
| Feature | Long-Term Investing | Day Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Build wealth over decades | Generate profit from short-term price movements |
| Time Horizon | 5+ years (often 20-40) | Same day to a few weeks |
| Hands-On Level | Low (Set and forget) | Extremely High (Constant monitoring) |
| Risk Profile | Lower (Volatility smooths out) | Very High (Leverage and volatility) |
| Best For | Retirement, financial independence | Speculators, full-time traders |
Conclusion
Ultimately, successful long-term investing is less about picking the next hot stock and more about discipline, diversification, and patience. The right strategy acts as a force multiplier for your financial intelligence, turning regular savings into significant wealth through the relentless power of compound interest. While the choice of assets depends on your individual risk tolerance and timeline, the act of starting—and staying consistent—is the most critical step toward financial empowerment. The clarity gained from having a plan and sticking to it through market cycles is invaluable. Start by automating contributions to a low-cost index fund in a tax-advantaged account, and then level up your knowledge and portfolio as you become more comfortable.
Ready to put your investment plan into action? The best way to start is to open an account with a broker that fits your strategy. Whether you’re a DIY investor or prefer a guided approach, the platform you choose is key. Check out our in-depth reviews of the Best Online Brokers and Investment Platforms to find your perfect match and begin your journey today.
Related Terms
- Compound Interest: The process where the earnings on an investment themselves earn interest over time, leading to exponential growth. It’s the engine of long-term investing.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: The strategy of investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the share price. This reduces the impact of volatility and lowers the average cost per share over time.
- Asset Allocation: The implementation of an investment strategy that attempts to balance risk versus reward by adjusting the percentage of each asset in a portfolio according to the investor’s risk tolerance, goals, and investment time frame.
- Diversification: The risk management strategy of mixing a wide variety of investments within a portfolio to minimize the impact of any single asset’s performance on the overall portfolio.