What Is 0x Protocol, How It Works, and Why It's Key to DeFi
0x Protocol is the open-source infrastructure powering the decentralized exchange of assets on the Ethereum blockchain and beyond. Think of it not as a single app, but as the fundamental plumbing that enables developers to build their own peer-to-peer trading applications, from simple token swaps to sophisticated professional-grade dashboards. For traders and investors in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia navigating the burgeoning world of decentralized finance (DeFi), understanding 0x is key to comprehending how trustless, global markets for digital assets actually function under the hood.
For crypto investors and traders in regions with mature financial markets like the US, UK, Canada, and Australia, 0x Protocol represents a foundational piece of DeFi infrastructure, enabling seamless and non-custodial trading of thousands of tokens directly from a wallet like MetaMask, bypassing traditional centralized exchanges.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Definition | An open-source, permissionless protocol built on Ethereum that facilitates the peer-to-peer exchange of digital assets through a system of off-chain order relay and on-chain settlement. |
| Also Known As | 0x, ZRX Protocol |
| Main Used In | Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), Tokenized Asset Trading |
| Key Takeaway | 0x separates the act of finding a trading counterparty (off-chain) from the final execution of the trade (on-chain), creating a hybrid model that is both highly efficient and fully trust-minimized. |
| Formula | N/A (Protocol, not a metric) |
| Related Concepts |
What is the 0x Protocol
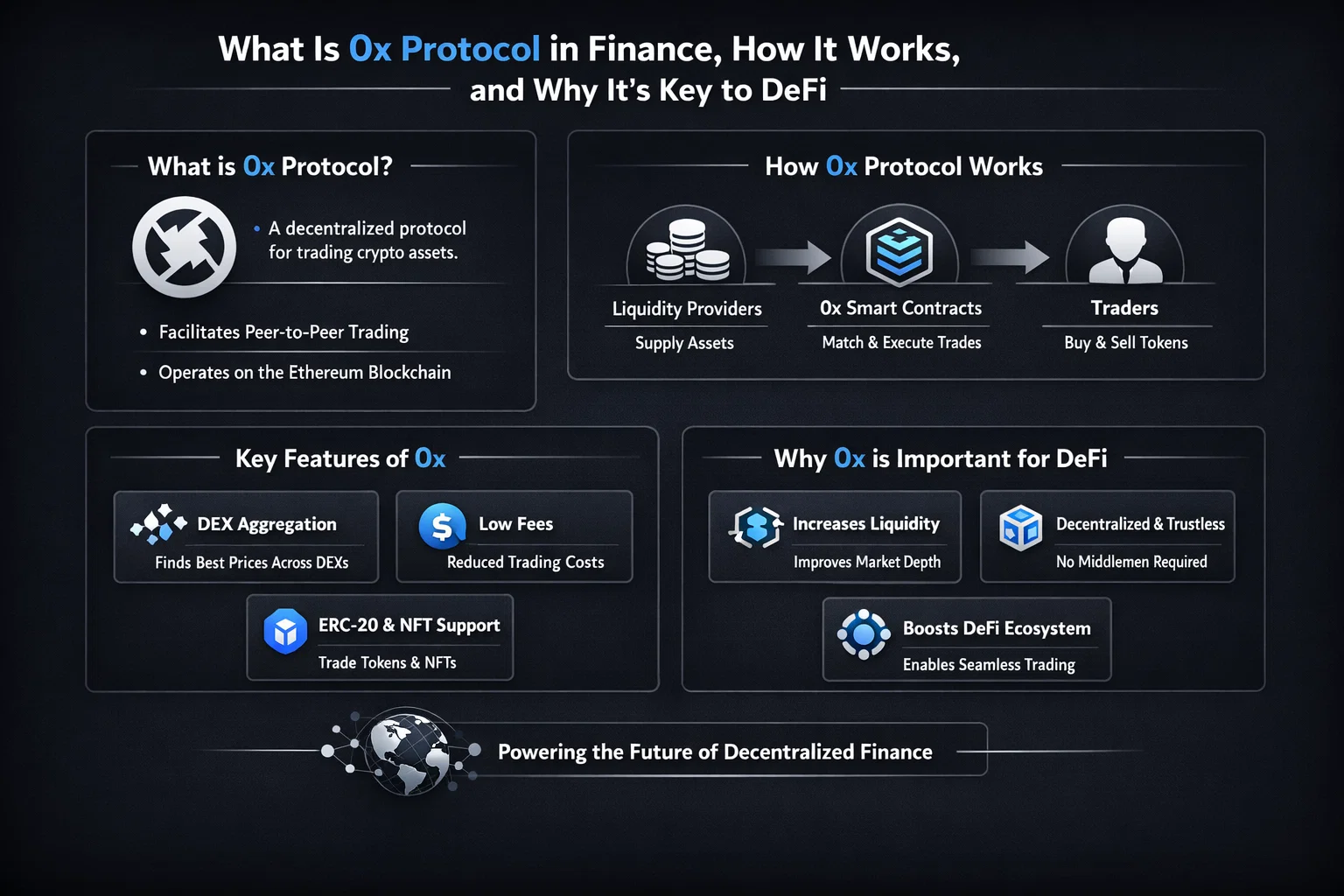
At its core, 0x Protocol is a set of smart contracts and standardized message formats (APIs) that enable any developer to build a decentralized exchange. Unlike a traditional centralized exchange like Coinbase or a single automated market maker (AMM) like Uniswap, 0x is not an application you use directly. Instead, it’s the foundational code that many applications—called “relayers”—use to offer trading services.
Imagine a stock trading protocol that standardized how buy and sell orders are communicated between any brokerage firm, allowing them to share a global pool of liquidity. 0x does this for the Ethereum blockchain and other EVM-compatible chains. It solves a critical problem in early DeFi: how to trade tokens without giving up custody of your assets (decentralized) while still achieving low fees and fast execution (efficient). Its native utility and governance token is ZRX.
Key Takeaways
The Core Concept Explained
The protocol’s innovation lies in its division of labor between off-chain and on-chain activities.
- Order Creation (Off-Chain): A trader signs an order—specifying token pair, amount, price, and expiry—using their private key. This creates a cryptographically secure message, not a blockchain transaction. It costs no gas.
- Order Relay (Off-Chain): This signed order is sent to a “relayer.” A relayer is like a bulletin board or a specialized search engine for 0x orders. They can host an order book, aggregate orders, and charge fees for their service.
- Order Filling (On-Chain): Another trader (or an automated bot) finds this order on a relayer. To execute it, they submit a “fill” transaction to the 0x smart contracts on the blockchain. The contract verifies the order’s signature and validity, then atomically swaps the tokens between the two parties. This step requires gas.
This model is efficient because only the final, successful trade burdens the Ethereum network, unlike fully on-chain order books which require constant, expensive updates.
Why is the 0x Protocol Important
The 0x protocol matters because it solves core limitations in decentralized trading, directly benefiting end-users and the DeFi ecosystem.
- For Traders: It provides better prices through liquidity aggregation. Instead of checking multiple DEXs, a trader using a 0x-based aggregator like Matcha gets the best available rate across many sources in one click. It also allows for more advanced order types (like limit orders) which are often missing from simple AMMs.
- For Developers: It offers plug-and-play exchange functionality. A developer building a new wallet, NFT platform, or investment DAO can integrate 0x’s smart contracts to enable in-app trading without building their own exchange from scratch. This saves immense time and security audit costs.
- For the DeFi Ecosystem: It enhances liquidity fragmentation by creating a shared communication layer. This composability is a cornerstone of DeFi’s innovation, allowing different protocols to seamlessly interact, creating more robust and efficient financial markets.
For a trader in the US or UK used to the order books of the NYSE or LSE, 0x-based applications provide the closest DeFi equivalent, offering familiar concepts like limit orders while maintaining the non-custodial security of crypto.
The Evolution & Architecture of 0x v4
The 0x Protocol has undergone significant iterations. The launch of 0x v4 in 2021 marked a major architectural shift from a monolithic design to a modular one, dramatically improving flexibility, upgradeability, and feature development.
🛠️ Plugins (Extensible)
Custom, optional logic (e.g., oracle-based price feeds, TWAP orders). Anyone can create and attach plugins.
🧩 Feature Modules (Selectable)
Self-contained features like Limit Orders, AMM Pool swaps, or RFQ. Developers choose which to enable.
⚙️ Protocol Core (Immutable)
The foundational, audited settlement layer. Handles order validation, signature checking, and atomic token transfers.
Why v4 Matters:
- Faster Innovation: New trading features (like NFT auctions or dutch orders) can be built as standalone modules without touching the core, reducing risk and speeding deployment.
- Permissionless Extensions: The plugin system allows any developer to extend a 0x-based exchange’s functionality, fostering a rich ecosystem of tools.
- Reduced Gas Costs: Modular design means traders only pay for the features they use in a given transaction, optimizing gas efficiency.
- Future-Proofing: The core can remain static and secure, while the modules on top can evolve rapidly with market demands.
This evolution shows 0x’s commitment to being adaptable infrastructure rather than a fixed product, solidifying its role as a long-term building block for DeFi.
How to Use 0x Protocol
As an end-user, you interact with 0x through applications built on top of it. Here’s how to leverage it in your DeFi activity:
- Finding the Best Price: Use 0x-powered aggregators like Matcha or the 0x API integrated into wallets like MetaMask for swap functionality. When you swap tokens, these tools scan 0x relayers and other liquidity sources to give you the optimal rate.
- Setting Limit Orders: Platforms like TokenTango or features within aggregators allow you to set limit orders (e.g., “Buy ETH if it drops to $2,800”). Your order sits with a relayer until it’s filled, without you needing to monitor the market constantly.
- Trading Rare or New Tokens: Due to its open order book model, 0x can be effective for trading tokens that may have insufficient liquidity on major AMMs, as market makers can post specific bids and offers.
To start trading with the efficiency of 0x, you need a reliable web3 wallet. If you’re new, check out our guide on setting up and securing a MetaMask wallet, the most common gateway to DeFi applications in North America and Europe.
- Efficiency & Low Cost: Off-chain order relay drastically reduces blockchain congestion and gas costs for order placement and discovery.
- Liquidity Aggregation: Provides traders with the best possible price by tapping into a vast, aggregated pool of liquidity from multiple sources.
- Flexibility for Developers: Enables rapid development of bespoke trading applications, fostering innovation in the DeFi space.
- Non-Custodial Security: Users never give up control of their assets until the moment of atomic swap, eliminating counterparty risk.
- Advanced Order Types: Supports limit orders, RFQ (Request-for-Quote), and other complex order types not native to simple AMMs.
- Relayer Dependence: The ecosystem relies on third-party relayers to host and broadcast orders, which could, in theory, censor or front-run orders.
- Liquidity Fragmentation: While it aggregates, liquidity can still be spread across many relayers, sometimes making AMMs better for small, instant swaps of common pairs.
- On-Chain Settlement Gas: The final settlement transaction still requires a gas fee, which can be high during Ethereum network congestion.
- Complexity for New Users: The conceptual model is less straightforward than a simple “Swap” button on a Uniswap-like interface.
- MEV Vulnerability: Like all public blockchain transactions, order fills can be susceptible to Miner Extractable Value strategies like front-running.
ZRX Token: Utility and Governance in the 0x Ecosystem
While traders don’t need ZRX to swap tokens, the token is the lifeblood of the protocol’s decentralized governance and economic sustainability. Its role has evolved significantly since launch.
Protocol Governance
ZRX holders can propose and vote on upgrades to the 0x Protocol smart contracts, treasury management, and key parameters. This moves control from the initial developers to a global community of stakeholders.
Staking & Relayer Fees
In previous versions, relayers could share fees with ZRX stakers. While the model in v4 is more flexible, ZRX remains the envisioned currency for ecosystem incentives, potentially rewarding liquidity providers or data curators.
Security & Coordination
The token aligns incentives. Holding ZRX means you have a vested interest in the protocol’s security, efficiency, and adoption, encouraging active participation in governance.
Governance in Action: The 0x DAO
Governance decisions are made via the 0x DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization), facilitated by platforms like Snapshot and Tally. Examples of past proposals include:
- Approving multi-chain expansion grants to deploy 0x on new networks like Polygon and Fantom.
- Allocating treasury funds to bug bounty programs and security audits.
- Ratifying the technical specification and budget for the 0x v4 upgrade.
For Investors: The value of ZRX is intrinsically linked to the usage and success of the 0x Protocol itself. As more volume flows through 0x-based applications and the DAO makes impactful decisions, the demand to participate in governance can influence the token’s utility value.
0x Protocol in the Real World: A Case Study
A prime example of 0x’s power is its role in the NFT marketplace boom. Before native marketplaces like Blur or OpenSea’s Seaport protocol matured, many platforms used 0x to facilitate NFT trades. Why? Because 0x’s flexible order schema could easily handle unique, non-fungible assets (ERC-721) alongside fungible tokens (ERC-20) for payment.
For instance, a user could list a CryptoPunk for 70 ETH on a 0x-integrated marketplace. This order would be broadcast across the relayer network. A buyer, seeing the order, could fill it by submitting a transaction that would atomically transfer the 70 ETH from their wallet to the seller’s and the CryptoPunk from the seller’s wallet to theirs, all in one click, without ever depositing the asset into a central marketplace escrow. This demonstrated 0x’s adaptability beyond simple token swaps and its utility in creating complex, trustless marketplaces for digital assets.
0x API: The Hidden Engine Powering Major DeFi Apps
Beyond the public-facing protocol, 0x Labs provides a robust, professional API that is arguably the most impactful product for mainstream DeFi adoption. This isn’t for hobbyists—it’s the enterprise-grade engine used by industry leaders.
Who Uses the 0x API and Why?
- Wallets (MetaMask, Coinbase Wallet): When you hit “Swap” in your wallet, it’s often the 0x API sourcing liquidity and routing your trade for the best price across dozens of DEXs and market makers.
- DeFi Platforms (Yearn, Balancer): Use the API for efficient asset rebalancing and internal token swaps within their strategies.
- NFT Marketplaces & Games: Integrate token-swapping functionality so users can buy in-game assets or pay fees without leaving the app.
- Traditional FinTech Apps: Companies exploring crypto integration use the API as a secure, compliant on-ramp to decentralized liquidity.
The Value Proposition for Integrators:
✅ Liquidity Aggregation: One integration taps into the deepest aggregated liquidity across Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche, and more.
✅ Reliability & Uptime: Enterprise-grade SLA and infrastructure, crucial for mainstream applications.
✅ Regulatory Compliance Tools: Built-in features for screening transactions (like OFAC compliance) are vital for regulated entities.
✅ No Protocol Management: Integrators don’t need to run relayers or manage smart contracts; they just call an API.
This commercial API is a key revenue generator for 0x Labs and demonstrates the protocol’s real-world utility at scale. It’s the bridge between the decentralized protocol and the centralized applications that billions of users trust.
0x Protocol vs Uniswap
| Feature | 0x Protocol (Off-Chain Order Book) | Uniswap (Automated Market Maker – AMM) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Off-chain signed orders matched by takers; on-chain settlement. | On-chain liquidity pools with prices set by a constant product formula (x*y=k). |
| Liquidity Source | Professional market makers, other DEXs, aggregated pools. | Crowdsourced from liquidity providers (LPs). |
| Price Discovery | Through market maker bids/offers and order matching. | Algorithmically determined by pool ratios; can have slippage. |
| Gas Efficiency | High for makers (off-chain), gas paid only by taker on settlement. | Gas paid by every swapper and liquidity provider for each interaction. |
| Best For | Large orders, limit orders, price-sensitive traders, rare assets. | Small to medium instant swaps, passive liquidity provision, simplicity. |
Conclusion
Ultimately, the 0x Protocol is the indispensable backbone for sophisticated, efficient decentralized trading. While end-users may not interact with it directly, its benefits—better prices, advanced orders, and seamless in-app trading—are felt across the DeFi landscape. As with any tool, it has trade-offs, primarily its reliance on relayers and the persistent cost of on-chain settlement. However, its design as open, composable infrastructure ensures it will continue to evolve alongside the broader blockchain ecosystem. For any serious DeFi participant, understanding 0x means understanding how the markets of the future are being built today.
Ready to explore trading on 0x-powered applications? Your first step is choosing a secure and user-friendly DeFi wallet. We’ve reviewed the top wallets for security, ease of use, and chain support to help you safely navigate the world of decentralized exchanges.
Related Terms:
- Decentralized Exchange (DEX): 0x is a protocol for building DEXs.
- ZRX Token: The native governance and utility token of the 0x ecosystem, used for protocol upgrades and fee payments.
- MEV (Miner Extractable Value): A concern for all on-chain trading, including orders filled via 0x.
- RFQ (Request for Quote): A trading model where a trader requests a price quote from specific market makers, often used in 0x for large, OTC-like trades.
- ERC-20: The token standard on Ethereum that 0x primarily facilitates trading for.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recommended Resources
- Official 0x Website & Docs: The definitive source for technical information.
- 0x Labs Blog: For updates on protocol development and ecosystem news.
- Matcha: A popular, user-friendly trading interface built on 0x.
- Investopedia: Decentralized Finance (DeFi): For foundational knowledge on the broader context.