How an Investment Planner Helps to Grow Your Wealth
Feeling overwhelmed by market volatility and unsure if your investments are on the right track? An investment planner provides the clarity and strategy you need. This guide will walk you through the entire process of how a planner works, from the initial consultation to ongoing portfolio management, so you can confidently build and protect your wealth.
For individuals in the US, UK, and Canada, working with a qualified financial planner can help you navigate local tax-advantaged accounts like 401(k)s, IRAs, ISAs, and TFSAs, ensuring your wealth grows in the most efficient way possible.
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Goal | To understand the role, process, and benefits of working with an investment planner to achieve long-term financial growth. |
| Skill Level | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Time Required | Ongoing relationship (Initial setup: 1–4 weeks) |
| Tools Needed | Information on your income, expenses, debts, assets, and financial goals. |
| Key Takeaway | An investment planner provides more than stock picks; they offer a comprehensive strategy, behavioral coaching, and ongoing management that can significantly increase your probability of financial success. |
| Related Concepts |
Why Partnering with an Investment Planner is Crucial
Many people believe investing is about finding the next big stock. In reality, the greatest threat to your wealth isn’t missing a hot tip, it’s a lack of a coherent plan, emotional decision-making, and the silent erosion of taxes and inflation. An investment planner solves this by providing a disciplined, structured approach to growing your wealth. They act as your personal Chief Financial Officer, ensuring every dollar has a purpose and is working efficiently toward your life goals.
The outcome is not just a larger portfolio balance, but profound financial clarity and confidence. You’ll have a roadmap that anticipates market downturns, leverages tax strategies, and adapts to your changing life, turning the complex world of finance from a source of stress into a tool for achieving your dreams.
Key Takeaways
What You’ll Need Before You Start
Engaging a planner is a collaborative process. To get the most out of it, come prepared.
Knowledge Prerequisites: A basic understanding of your own financial situation and a general idea of your long-term aspirations (e.g., “I want to retire at 65,” “I want to fund my child’s education”). You don’t need to be a finance expert, that’s their job.
Data & Document Requirements:
- Recent pay stubs and tax returns
- Announcements for all bank, brokerage, and retirement accounts
- Details on debts (mortgages, loans, credit cards)
- Insurance policies (life, disability, property)
- A rough estimate of your monthly budget
Tools & Platforms: While the planner will have their own software, you can use a tool like Personal Capital to get a head start on aggregating your financial data.
To easily pull all your financial data into one place, you’ll need a reliable aggregation tool. Many of the best robo-advisors and financial apps, like Mint or the aforementioned Personal Capital, offer this for free. This preparation will make your first meeting with a planner incredibly efficient.
How an Investment Planner Grows Your Wealth
Step 1: The Discovery & Goal-Setting Session
The process begins with a deep dive into your entire financial life. Your planner will ask questions about your income, expenses, assets, liabilities, family situation, and, most importantly, your dreams and fears. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding what you want your money to do for you.
Pro Tip: Be completely open and honest. The more your planner knows, the more tailored and effective your plan will be. There is no judgment, only a desire to build a strategy that fits you.

Step 2: Data Analysis & Risk Assessment
Here, the planner crunches the numbers. They analyze your cash flow, net worth, current investments, and insurance coverage. Crucially, they will have you complete a formal risk tolerance questionnaire. This scientifically-grounded assessment determines your ability and willingness to withstand market fluctuations, which is the bedrock of your investment strategy.
Common Mistake to Avoid: Overestimating your risk tolerance. Many people say they are aggressive investors until a market crash happens. A good planner helps you find a sustainable risk level that you can stick with through all market cycles.
Step 3: The Personalized Financial Plan & Asset Allocation
This is the deliverable. Your planner presents a comprehensive plan that outlines specific recommendations. The core of the investment strategy is your asset allocation—the percentage of your portfolio dedicated to stocks, bonds, and other assets. This allocation is designed to target the returns you need to meet your goals while respecting the risk level you identified in Step 2.
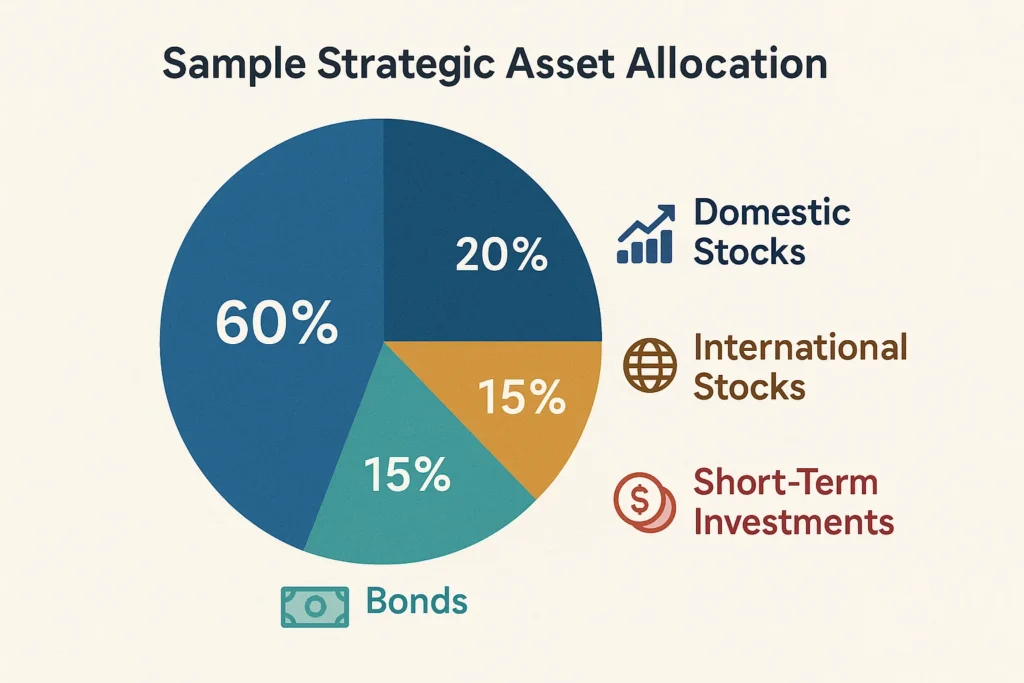
Example Allocation: For a 40-year-old with a moderate risk tolerance saving for retirement, an allocation might be: 60% Domestic Stocks, 20% International Stocks, 15% Bonds, 5% Short-Term Investments.
Step 4: Implementation & Portfolio Construction
With the plan approved, the planner executes it. This involves selecting specific investments (e.g., low-cost ETFs, mutual funds) that fulfill the asset allocation. They handle all the paperwork and transactions to rebalance your existing portfolio or fund a new one. A key part of their value here is focusing on low-cost, tax-efficient investments to maximize your net returns.
Step 5: Ongoing Monitoring, Rebalancing, and Coaching
The work doesn’t stop after the portfolio is built. This is the most critical phase for long-term growth. Your planner continuously monitors your portfolio and the markets. When your asset allocation drifts from its target (e.g., stocks have a great year and now comprise 70% instead of 60%), they rebalance—selling high and buying low—to maintain your target risk level. They also provide behavioral coaching during market downturns, stopping you from making panic-driven decisions.
How to Use Your Financial Plan in Your Daily Life
The plan is not a document to be filed away. It’s a living guide.
Scenario 1: Market Downturn: Instead of panicking and selling, you refer to your plan. It anticipated these cycles. Your planner contacts you, reiterates the long-term strategy, and may even see this as a rebalancing opportunity. This saves you from locking in losses.
Scenario 2: Receiving a Windfall (Bonus, Inheritance): You have a pre-established protocol. Your planner helps you integrate the new funds into your plan according to your asset allocation, ensuring it’s invested wisely rather than spent impulsively.
Case Study: “A client, Sarah, was tempted to sell all her stocks during the March 2020 crash. Her planner reminded her of their long-term plan, the purpose of her emergency fund, and the historical context of market recoveries. By staying invested, Sarah not only recovered her losses by the end of the year but saw her portfolio grow over 50% from its pre-pandemic highs, perfectly aligning with her retirement timeline.”
Common Mistakes When Choosing an Investment Planner
Pitfall 1: Choosing a planner based solely on cost. The cheapest option may not provide comprehensive service. Solution: Focus on value. A planner who saves you from one major behavioral mistake or optimizes your taxes can be worth many times their fee.
Pitfall 2: Not understanding how the planner is paid. This can lead to conflicts of interest. Solution: Ask directly: “Are you a fiduciary?” and “How do you get compensated?” Prioritize fee-only planners (paid directly by you) over fee-based planners (who may also earn commissions) to minimize conflicts. You can find fee-only planners through NAPFA.
Pitfall 3: Being a passive client. The relationship is a two-way street. Solution: Be engaged, ask questions, provide updated information promptly, and be open to advice.
Your Checklist for Vetting a Financial Planner
Don’t just pick the first name you find. Due diligence is critical.
- Verify Credentials: Check for CFP® certification and a clean record on FINRA’s BrokerCheck.
- Understand the Fee Structure: Ask for a full disclosure of all fees in writing. Is it Assets Under Management (AUM), hourly, flat fee, or commission?
- The Fiduciary Question: This is non-negotiable. Ask: “Will you sign a fiduciary oath committing to act in my best interest at all times?”
- Ask About Their Typical Client: Do they usually work with people like you (similar age, net worth, profession)?
- Request a Sample Plan: Ask to see an anonymized sample financial plan to gauge the depth and clarity of their work.
- Interview 3 Candidates: Compare their communication style, philosophy, and how well you connect with them personally.
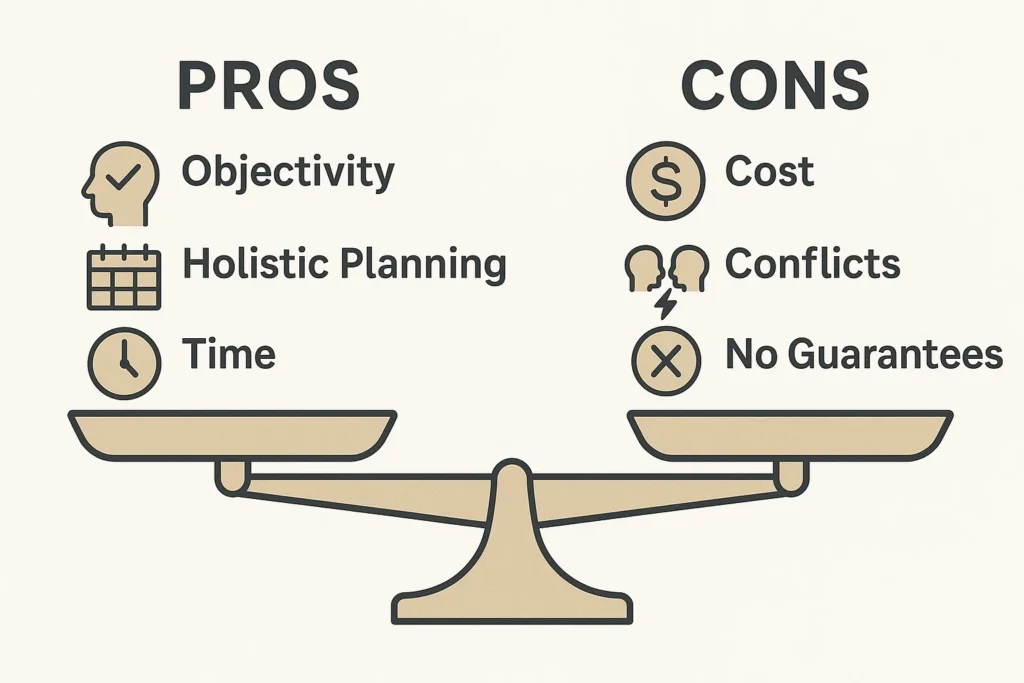
- Objective Guidance Removes emotion from investing, the number one wealth destroyer.
- Holistic Approach Integrates investing with tax, retirement, and estate planning.
- Time Savings Frees you from the daily burden of managing and researching investments.
- Expertise Access Provides access to sophisticated strategies and research.
- Accountability Keeps you on track toward your goals with regular check-ins.
- Cost Fees can eat into returns over time.
- Not All Are Equal The quality of advice varies greatly.
- Potential Conflicts If not a fiduciary, may recommend products for commissions.
- No Guarantees Cannot guarantee market-beating returns.
- Finding the Right Fit The search and vetting process can be time-consuming.
The Alpha of a Financial Planner: Justifying the Fee
A 1% annual fee might seem high, but a good planner can add well over that in “value alpha.” The Vanguard study on Advisor’s Alpha quantifies this, suggesting a good advisor can add about 3% in net returns per year through:
- ~1.50% from Behavioral Coaching: Stopping you from panic-selling.
- ~0.45% from Tax-Efficient Investing: Placing assets in the right accounts.
- ~0.75% from Rebalancing & Asset Allocation: Maintaining discipline.
- ~0.70% from Cost-Effective Investments: Using low-cost funds.
When you view the fee as an investment that yields a higher net return, the value proposition becomes clear.
Taking It to the Next Level
For those who have a basic plan in place, a skilled planner can delve into more sophisticated strategies.
Tax-Loss Harvesting: This involves selling investments at a loss to offset taxes on gains and income. Advanced platforms and advisors automate this, but a human planner can add nuance to the strategy. Learn more about the basics on the IRS website.
Options Overlay Strategies: Using covered calls or cash-secured puts to generate additional income from an existing portfolio, a tactic for more experienced, risk-tolerant investors.
Investment Planner vs Robo Advisor
It’s easy to confuse different financial roles. Here’s a clear breakdown:
| Feature | Investment Planner | Robo-Advisor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Holistic financial life & goals (retirement, tax, estate). | Automated, low-cost portfolio management. |
| Service Model | Personalized, human-led advice and coaching. | Algorithm-driven, entirely digital experience. |
| Advice Includes | Comprehensive financial planning. | Basic investment allocation and rebalancing. |
| Best For | Those needing comprehensive planning & behavioral guidance. | Hands-off investors with straightforward goals. |
Conclusion
You now understand that an investment planner’s true value lies not in secret stock tips, but in providing a disciplined, holistic framework for your financial life. They are your strategist, behavioral coach, and accountability partner, guiding you through market noise and life changes. The key is to find a qualified fiduciary who aligns with your values and goals.
Start today by researching 2-3 fee-only financial planners in your area or who offer virtual services. Schedule introductory calls to see who you connect with best.
To make the search for a qualified professional effortless, use the free matching services from NAPFA (for fee-only planners) or the CFP Board. And if you’re looking for a platform to start investing on your own while you search, check out our reviews of the best online brokers for beginners.
Related Guides You Should Read Next:
- Fee-Only vs. Fee-Based Advisors: What’s the Difference?
- A Beginner’s Guide to Asset Allocation
- How to Calculate Your True Risk Tolerance