A Roth IRA (Individual Retirement Account) is one of the most widely accepted capital allocation vehicles in the United States, delivering unique perks for pension reserves. However, with so many possibilities available, how do you find the best Roth IRA for your needs? This complete lead will examine how to find the best Roth IRA accounts, their pros and cons, and answer frequently asked inquiries to benefit you and create an enlightened resolution.
A Roth IRA is most beneficial when you expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement. Because you fund a Roth IRA with money you’ve already paid taxes on, eligible withdrawals—including any investment gains—can be taken out tax-free in retirement.
Key Takeaways
What Is a Roth IRA
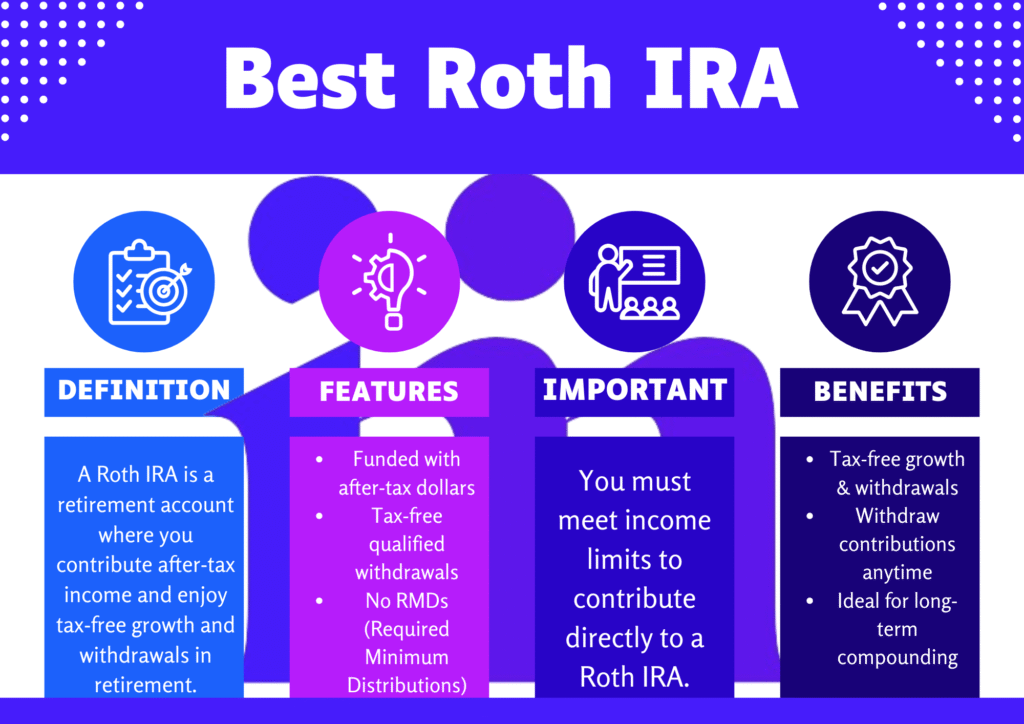
A Roth IRA is a pension retirement fund ledger that allows you to give after tax dollars and, in revenue, delight in tax free expansion and tax free withdrawals in superannuation. Unlike established IRAs, where inputs are made with pretax dollars and taxed upon disbursement, the best Roth IRA provides a distinct tax structure. You fund the bank account with wealth that has already been taxed, but when you withdraw the funds during pension (provided you meet a certain state), you won’t pay taxes on the earnings.
When I opened my first Roth IRA, I was earning an entry-level salary and didn’t think much of retirement. But locking in a low tax rate in my 20s ended up being one of the smartest financial moves I’ve made—it gave my investments decades to grow tax-free.
How to Find the Best Roth IRA
Finding the best Roth IRA can be a daunting task, especially with so many choices available. Here’s a step by step guide to benefit you: Pick the best Roth IRA for your superannuation objectives.
1. Compare Investment Options
The best Roth IRA accounts extend a wide range of funding selections. These typically embrace stocks, bonds, ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds), mutual money, and even individual real estate or other alternative securities. Some Roth IRAs are more adaptable, delivering more funding possibilities, while others may possess constrained choices.
- Robo Advisors: Some platforms provide managed Roth IRAs through robo advisors that employ algorithms to decide on securities based on your risk tolerance and fiscal aims.
- Brokerage Accounts: If you wish for full supervision over your funding choices, some Roth IRA providers provide brokerage accounts, allowing you to purchase and transfer stocks, ETFs, and mutual money.
Look for a Roth IRA provider that offers no account maintenance fees, a wide range of low-cost index funds, and automated rebalancing tools. These features help maximize long-term returns while minimizing hands-on management.
2. Audit The Expenses
Charges can significantly affect your returns over time, so it’s vital to assess the fee structure of any Roth IRA provider you’re considering. Generally, charges are divided into three divisions:
- Account Charges: Annual maintenance or setup charges.
- Funding Charges: Expenses related to the assets you select, such as mutual fund direction costs or cost ratios.
- Exchanging Charges: Some Roth IRA accounts may charge you every time you purchase or trade an asset allocation.
Opt for a Roth IRA provider with smaller expenses to ensure your funds perform harder for you in the extended run.
For 2025, individuals can contribute up to $7,000 annually to a Roth IRA, or $8,000 if they’re age 50 or above, as long as their income falls within the allowed thresholds.
3. Look for User Friendly Platforms
Many individuals overlook the ease of employment when selecting the best Roth IRA, but it’s vital to think about the user’s skills. A base with a clean, intuitive interface and supportive customer endorsement can make managing your pension reserves much more convenient. Look for providers that extend mobile apps and online access, so you can review your bank account and adjust your assets on the go.
4. Think About the Contribution Limits
As of 2025, the Roth IRA donation control is $6,500 for people under the age of 50 and $7,500 for those 50 or older (with the excess sum being a “catch up” donation). However, the best Roth IRA accounts own the flexibility to form regular inputs without hidden charges or restrictions. form sure that the record you decide on allows you to donate up to the maximum limit.
A CNBC feature profiled a couple in their 30s who contributed regularly to Roth IRAs while living modestly. By maxing out their accounts annually and investing in index funds, they built a combined balance of over $400,000 in under 15 years—tax-free in retirement.
5. Judge The Account’s Result Record
While past achievement is not always indicative of future results, it can offer insight into the quality of the capital allocation possibilities available in a Roth IRA ledger. evaluate outcome metrics such as annual returns and the overall expansion of the ledger. This can support you to gauge whether the record is a stable option for your superannuation objectives.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✔ One of the most meaningful rewards of a Roth IRA is that qualified withdrawals are completely tax free. | ✘ There are annual donation caps ($6,500 or $7,500 if you are 50 or older), which might not be enough for those who want to give more for their pension. |
| ✔ Unlike established IRAs, you can donate to a Roth IRA even after you reach the age of 70 ½, as long as you meet the earnings requirements. | ✘ Unlike conventional IRAs, Roth IRA shares are made with after tax dollars, so you do not get a tax deduction for donations in the current year. |
| ✔ Established IRAs require you to commence taking RMDs at age 73. | ✘ While you can withdraw your shares without penalties, early disbursement of earnings before age 59 ½ may affect penalties and taxes unless you meet particular exceptions. |
| ✔ You can withdraw your donations (but not earnings) at any time without penalty. | ✘ The salary limit for individual filers is $153,000, and for married couples filing jointly, it’s $228,000. If your revenue exceeds these caps, you may not be eligible to give directly to a Roth IRA. |
Individuals with higher incomes might be ineligible to make direct contributions to a Roth IRA due to IRS-imposed income limits. If your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds the IRS limits, consider a backdoor Roth IRA strategy—but be cautious of the pro-rata tax rule.
Conclusion
The best Roth IRA for you will depend on your private economic aims, risk tolerance, and desires. Whether you decide on a self-directed Roth IRA with a brokerage bank account or one managed by a robo advisor, it’s vital to evaluate components like asset allocation selections, charges, and ledger flexibility. By understanding the pros and cons of Roth IRAs and answering some of the most standard queries, you’ll be better equipped to decide on the appropriate pension ledger for your needs.
Picking the best Roth IRA is not just about finding the lowest expenses or the most attractive asset allocation selections. It’s about understanding how a Roth IRA fits into your overall monetary scheme and superannuation targets. With the appropriate Roth IRA, you can obtain full advantage of tax free expansion and tax free withdrawals in pension, helping you fulfill economic protection and calm of mind.
