In today’s financial world, access to credit plays a pivotal role in helping individuals and businesses manage expenses, build assets, and handle unexpected costs. One of the most common ways this access is provided is through credit loans. But what is credit loans, exactly? How do they function, and what should borrowers be aware of before applying?
This comprehensive guide explains how credit loans work, explores various types, outlines the advantages of credit loans, highlights potential risks, and answers frequently asked questions, helping you make informed decisions at every financial stage.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
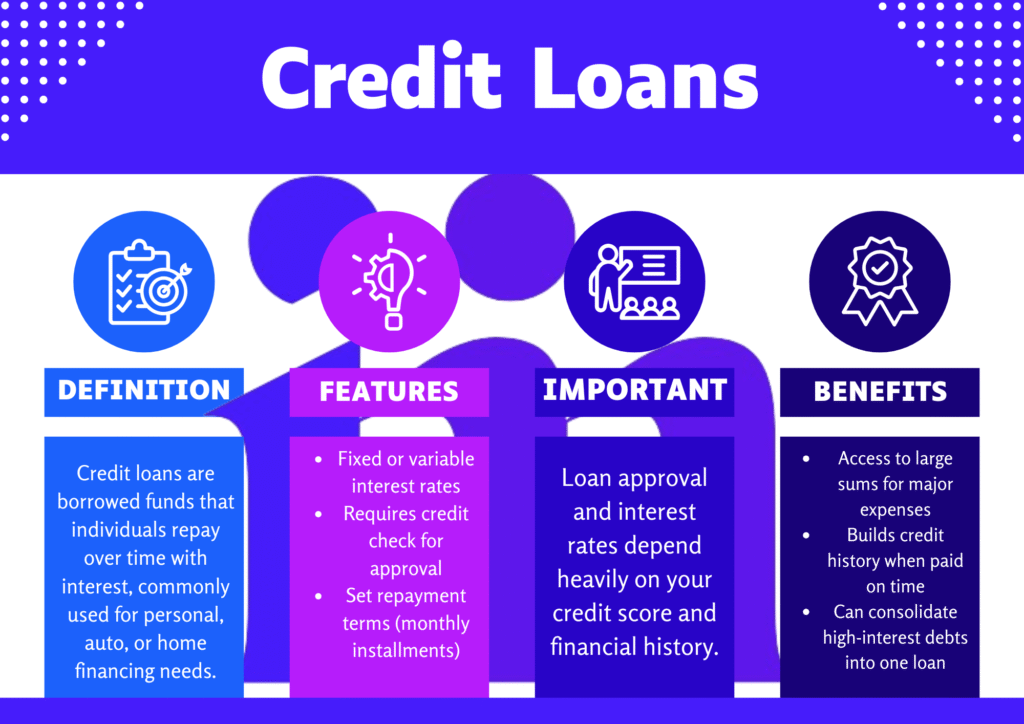
What Is a Credit Loan
A credit loan refers to a financial agreement where a borrower receives funds from a lender and agrees to repay it over time, typically with interest. Depending on your credit profile and the lender’s terms, credit loans may require collateral or be issued without it.
Unlike revolving credit (like credit cards), most credit loans involve fixed repayment terms and a lump-sum disbursement.
Not all credit loans are created equal, always verify your lender’s legitimacy, especially when applying online. Scammers often disguise high-interest predatory loans under the label of personal loans.
How Credit Loans Work
It’s important to grasp the basics of how credit loans function before applying for one. Here’s how the process generally unfolds:
1. Application
You start by submitting your loan application to a financial institution like a bank, online lender, or credit union. You’ll need to provide personal, income, job, and debt-related information during the application.
2. Credit Check
Lenders assess your credit report and score to judge your trustworthiness; higher scores typically secure more favorable terms.
3. Approval and Offer
If approved, the lender provides a loan offer detailing the interest rate, repayment schedule, and other conditions.
4. Funding
After you agree to the loan terms, the funds are usually deposited straight into your account.
5. Repayment
The borrower repays the loan in monthly installments until the principal and interest are fully paid off.
As someone who once used a credit loan to consolidate high-interest credit card debt, I can say it was one of the smartest financial decisions I made. It simplified my payments, lowered my interest costs, and motivated me to stick to a monthly payoff schedule.
Types of Credit Loans
Various kinds of credit loans exist, each tailored to specific financial requirements:
1. Personal Loans
Unsecured loans that can be used for various purposes, medical bills, travel, or home repairs.
2. Auto Loans
Used to purchase vehicles. Auto loans are commonly backed by the car being financed.
3. Student Loans
Offered to help pay for college or higher education. These can be federal or private.
4. Mortgage Loans
Large, long-term loans used to buy homes. Secured by the property being purchased.
5. Payday Loans
Short-term, high-interest loans for emergency needs. Often seen as risky due to predatory terms.
6. Business Loans
Used to start or expand a business. Loans may require collateral or not, based on what kind they are and who’s lending.
Review your credit report in advance to avoid surprises before applying for a loan. Dispute any inaccuracies to ensure you get the best possible interest rate. You can access a free credit report every week at AnnualCreditReport.com.
Pros and Cons of Credit Loans
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✔ Fixed monthly payments help with budgeting. | ✘ Overborrowing can lead to debt traps. |
| ✔ Timely repayments can lead to a higher credit score over time. | ✘ Origination fees reduce actual loan value. |
| ✔ Versatile use: debt consolidation, emergencies, big purchases. | ✘ Missed payments damage credit history. |
| ✔ Builds financial discipline through structured repayments. | ✘ High interest rates for poor credit borrowers. |
Advantages of Credit Loans
There are many advantages of credit loans that make them attractive to borrowers:
1. Predictable Payments
Most credit loans have fixed monthly payments, which help with budgeting.
2. Lower Interest Rates (for Good Credit)
Borrowers with strong credit can access low APRs compared to credit cards.
3. Flexible Use
Personal loans offer flexibility, you can use them for nearly anything.
4. Credit Building
Making steady payments on a loan can positively impact your credit standing.
5. Lump-Sum Access
Immediate access to a large sum of money makes them ideal for big expenses.
According to Experian, the average U.S. personal loan debt in 2024 was $18,255, with an average interest rate of 11.3%, but borrowers with excellent credit scored rates below 7%.
Risks of Credit Loans
Despite their benefits, credit loans carry certain risks:
1. High Interest Rates (for Poor Credit)
Borrowers with low credit scores may face steep interest charges.
2. Debt Accumulation
Taking multiple loans or missing payments can lead to financial strain.
3. Origination Fees
Some lenders charge upfront fees, which reduce the amount you actually receive.
4. Impact on Credit Score
Late payments or defaulting on a loan harms your credit rating.
5. Collateral Risk
Secured loans put your asset at risk, your car or home could be repossessed if you fail to pay.
Mark, a 35-year-old software developer, had $12,000 in credit card debt with 22% APR. He took out a personal credit loan at 9.5% APR, used it to consolidate his credit cards, and saved over $2,000 in interest over the loan’s term, all while improving his credit score through consistent monthly payments.
Credit Loans vs. Revolving Credit
| Feature | Credit Loans | Revolving Credit (e.g., credit cards) |
| Borrowing Method | Lump-sum disbursement | Borrow as needed up to a limit |
| Repayment | Fixed monthly installments | Flexible, minimum monthly payments |
| Interest Rates | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Usage Flexibility | High (especially personal loans) | High but encourages overuse |
| Credit Impact | Builds credit with on-time payments | Same, but mismanagement is common |
Who Should Consider Credit Loans
- Individuals with stable income seeking fixed repayment terms
- Borrowers looking to consolidate debt
- People making large, one-time purchases
- Students and homeowners needing long-term financing
- Small business owners expanding operations
5 Smart Strategies to Use Credit Loans Effectively
- Shop Around for Rates: Use prequalification tools to compare offers without impacting your credit.
- Read the Fine Print: Understand fees, interest types (fixed vs. variable), and penalties.
- Avoid Over-Borrowing: Only borrow what you need and can repay comfortably.
- Set Up Autopay: Prevent missed payments and maintain a healthy credit score.
- Use for Asset-Building Purposes: Prioritize loans that help build value (e.g., home improvement, education).
Beware of payday loans labeled as “credit loans.” They often come with exorbitant fees and APRs exceeding 400%. They’re rarely a good long-term solution and can trap borrowers in a cycle of debt.
Final Thoughts
Credit loans can be powerful tools when used wisely, helping cover large expenses, consolidate high-interest debt, or invest in your future. But like any financial product, they require responsibility and planning. Understanding the types of credit loans, their advantages, risks, and repayment structure is the first step toward making them work in your favor.
Frequently Asked Questions
Related Readings
- How to Build Credit from Scratch
- Best Credit Cards for Beginners
- Credit Score Guide: What is a Good Score?
