Financial Planner vs Certified Financial Planner Who's Best
Feeling overwhelmed by your financial future and unsure where to turn for help? You’re not alone. The titles Financial Planner and Certified Financial Planner might sound similar, but understanding the difference is the key to finding trustworthy, competent advice. This guide will walk you through a step-by-step process to evaluate your needs, understand the crucial distinctions, and confidently select the right professional to help you achieve your goals.
For individuals and families across the US and Canada, navigating the financial advice landscape can be particularly confusing. Understanding the standards required of a CFP® professional in North America can protect you from conflicting advice and ensure your planner is held to a higher standard.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Goal | To choose the right financial professional by understanding the key differences between a generic Financial Planner and a Certified Financial Planner (CFP®). |
| Skill Level | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Time Required | 1-2 hours for initial research and vetting |
| Tools Needed | List of your financial goals, list of questions to ask, internet access for verification |
| Key Takeaway | Anyone can call themselves a Financial Planner, but only a CFP® professional is required to meet rigorous education, exam, experience, and ethics standards, including a fiduciary duty to act in your best interest. |

Why Choosing the Right Financial Professional is Crucial
Hiring a financial advisor is a deeply personal and impactful decision. The right one can help you build wealth, plan for retirement, and secure your family’s future. The wrong one can lead to high fees, unsuitable products, and eroded trust.
The Problem It Solves: The financial services industry is filled with confusing titles, salespeople masquerading as advisors, and potential conflicts of interest. Without a clear framework, you risk choosing an advisor who is not obligated to put your interests first.
The Outcome: By the end of this guide, you will be able to identify a qualified, ethical professional. This empowers you to build a productive, long-term partnership that translates your financial dreams into an actionable, successful plan.
Financial Planner vs. CFP®: A Detailed Side-by-Side Comparison
Understanding the high-level difference is one thing; seeing a direct comparison makes the choice crystal clear. The table below breaks down the key distinctions between a generic Financial Planner and a Certified Financial Planner™ professional.
| Feature | Generic Financial Planner | Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) |
|---|---|---|
| Regulation & Title | Largely unregulated title; anyone can use it. | Legally protected certification; granted only by the CFP Board. |
| Education Requirements | None required; may have other licenses (e.g., Series 6/7). | Must complete a CFP Board-registered education program on core financial planning topics. |
| Exam Requirement | No standardized exam for the planner title. | Must pass a comprehensive 6-hour exam with a ~65% pass rate. |
| Experience Requirement | None specifically for the title. | 6,000 hours of professional experience or 4,000 hours of apprenticeship. |
| Ethical Requirement | Varies; may be held to a suitability standard. | Must agree to the CFP Board’s Code of Ethics and Standards of Conduct. |
| Fiduciary Duty | Not guaranteed. Often held to a lower suitability standard. | Yes, required. Must act as a fiduciary when providing financial advice. |
| Scope of Advice | Often limited to specific products they are licensed to sell (e.g., insurance, securities). | Holistic; covers investments, insurance, taxes, retirement, and estate planning. |
| Ongoing Requirements | Continuing Education (CE) for specific licenses (e.g., Series, insurance). | 30 hours of CE every two years, including ethics. |
| Public Disciplinary History | Check via FINRA BrokerCheck (for brokers) or state insurance commissions. | Check via the CFP Board’s website and FINRA BrokerCheck. |
| Best For | Simple, transactional product needs (with extreme caution). | Comprehensive, ongoing financial planning and wealth management. |
A CFP® professional is subject to a rigorous Four E’s framework: Education, Examination, Experience, and Ethics. A generic Financial Planner is subject to none of these, making the CFP® a vastly more reliable and qualified choice for serious financial planning.
Beyond CFP®: A Quick Guide to Other Financial Certifications
The alphabet soup of financial credentials doesn’t end with CFP. While CFP is the gold standard for comprehensive planning, you might encounter other designations. Here’s what they mean:
- ChFC® (Chartered Financial Consultant): Very similar to the CFP in curriculum and rigor, also requiring extensive education and ethics. The key difference is the ChFC does not require a comprehensive final exam and has a stronger focus on insurance and estate planning.
- CFA® (Chartered Financial Analyst): The gold standard for investment analysis and portfolio management. CFAs typically work for institutional firms (like mutual funds or pension funds) rather than directly with individual clients on comprehensive plans.
- RIA (Registered Investment Advisor): This is not a credential, but a legal designation. An RIA is a firm or individual registered with the SEC or state authorities to provide investment advice. Many CFPs are also RIAs, which legally binds them to a fiduciary duty.
- CPA (Certified Public Accountant): The premier credential for accounting and tax preparation. Some CPAs also offer financial planning services, and those with the PFS (Personal Financial Specialist) credential have additional planning expertise.
When it matters: A CFP® is your best bet for a holistic life plan. A CFA is ideal for pure investment management. A CPA/PFS is excellent for tax-centric planning.
What You’ll Need Before You Start
Before you start interviewing potential planners, get your own financial house in order. This preparation ensures you can have a productive conversation and accurately assess their value.
Knowledge Prerequisites:
- A basic understanding of your own financial situation (income, debts, assets).
- A preliminary list of your short-term and long-term financial goals (e.g., buy a house, save for college, retire by 60).
Data & Tools:
- Clarity on Your Needs: Are you looking for comprehensive planning, or just investment management?
- Verification Tools: Bookmark the CFP Board’s website (letsmakeaplan.org) and FINRA’s BrokerCheck to verify credentials and disciplinary history.
To get a strong picture of your net worth, a critical first step for any organizer, you’ll need to organize your assets and liabilities. Using a budgeting app like Mint or You Need A Budget (YNAB) can automate this process. Alternatively, many of the best robo-advisors, like Betterment or Wealthfront, offer free net worth tracking tools that can be invaluable for this preparation.
How to Choose Between a Financial Planner and a CFP®: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
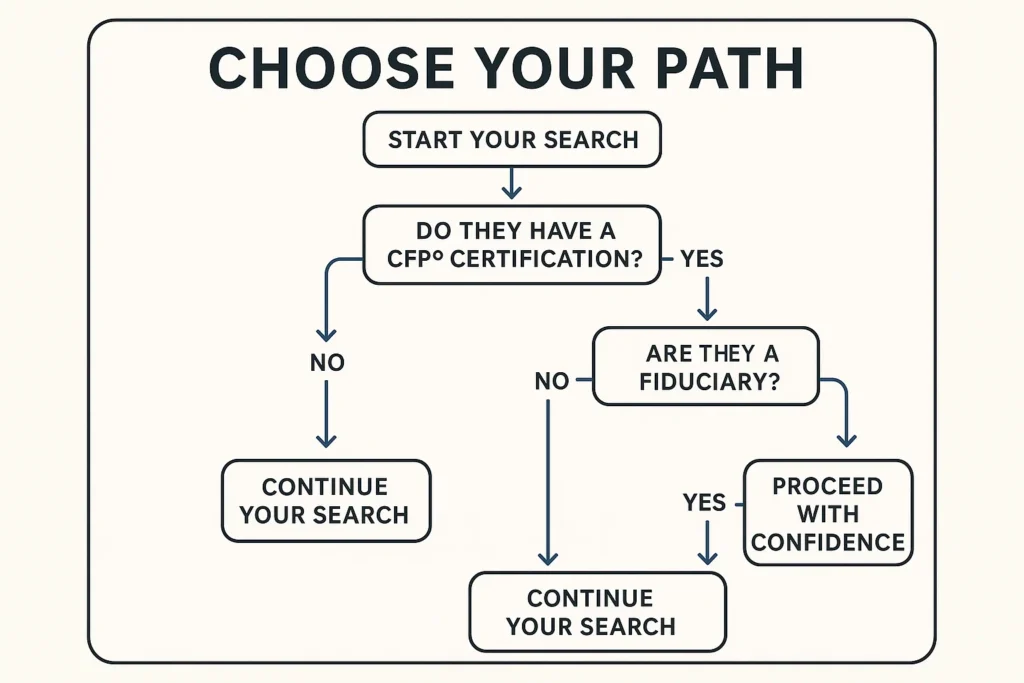
Step 1: Decode the Titles and Credentials
Not all financial professionals are created equal. Your first step is to understand what the titles mean.
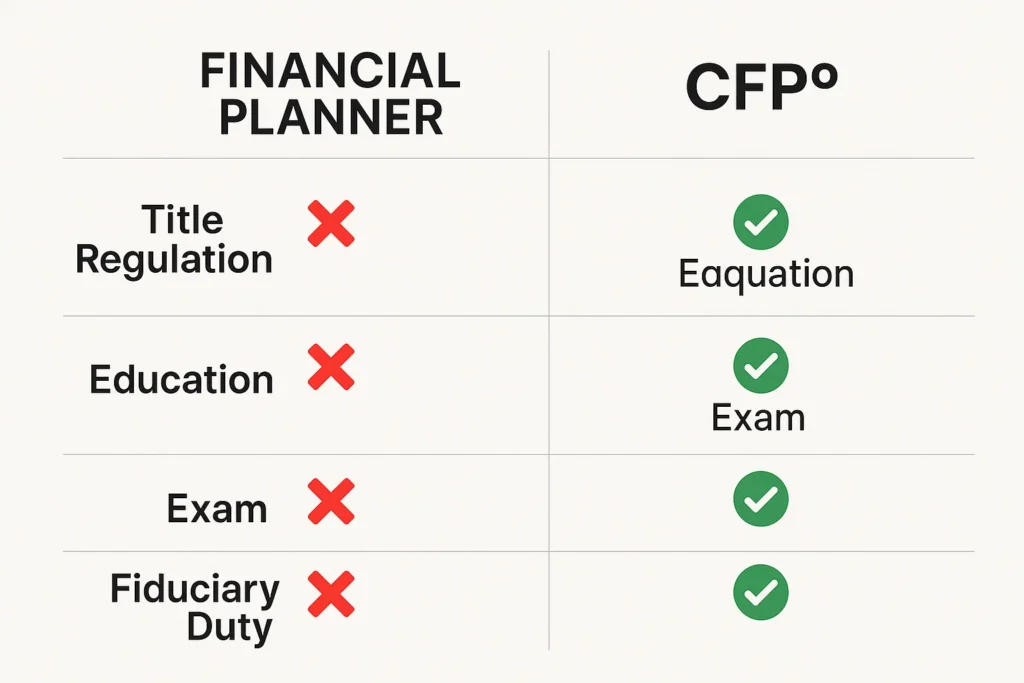
- Financial Planner: This is a general term with no legal protection. Anyone, regardless of education or experience, can use this title. They could be a highly experienced professional or an insurance salesperson with a weekend course.
- Certified Financial Planner (CFP®): This is a legally recognized certification with strict requirements enforced by the CFP Board. To earn and maintain the CFP marks, a professional must complete:
- Education: A rigorous college-level program on financial planning topics.
- Examination: Pass a comprehensive 6-hour exam.
- Experience: Log at least 6,000 hours of professional experience.
- Ethics: Adhere to strict ethical standards and a fiduciary duty.
Always look for a credential that requires a fiduciary duty. This legally obligates the advisor to put your interests ahead of their own.
Step 2: Understand the Fiduciary vs. Suitability Divide
This is the single most important concept in your search.
- Fiduciary Duty (CFP® Requirement): The advisor must provide advice that is in your best interest. They must avoid and disclose any conflicts of interest.
- Suitability Standard (Many non-CFP Planners): The advice and products recommended only need to be suitable for you at the time of the transaction. They do not necessarily have to be the best or lowest-cost option for you.
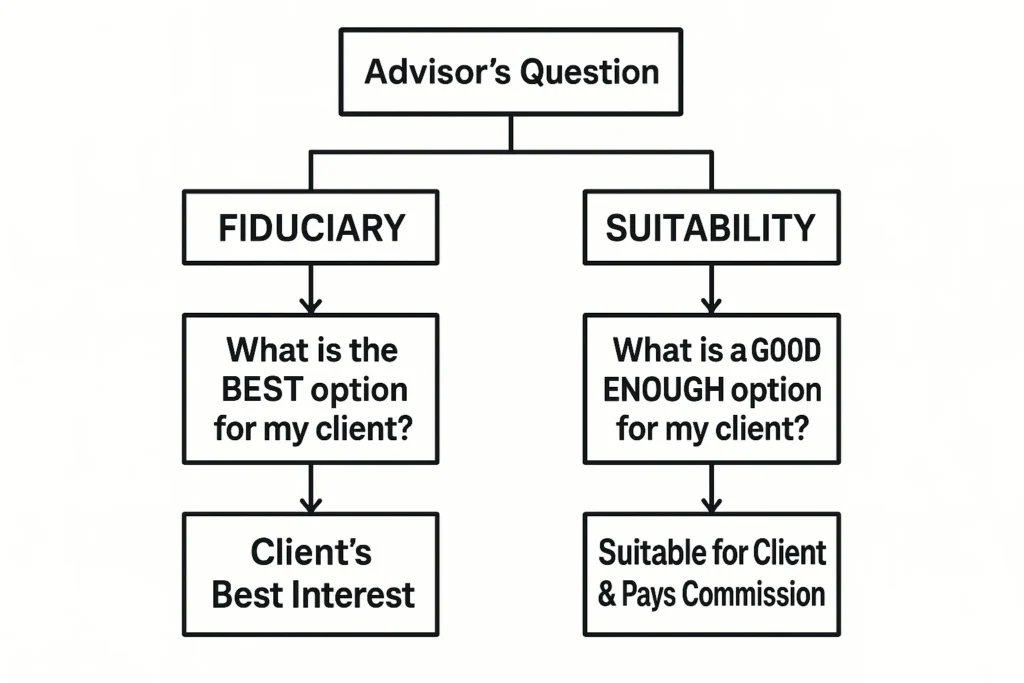
Common Mistake to Avoid: Assuming your advisor is a fiduciary. Many brokers and insurance agents are held only to a suitability standard, which can lead to recommendations that pay them higher commissions.
Step 3: Scrutinize How They Get Paid
Understanding compensation reveals potential conflicts of interest.
- Fee-Only (CFP®s often use this model): Paid directly by you, via hourly rates, flat fees, or a percentage of assets under management (AUM). This model has the fewest inherent conflicts.
- Commission-Only: Paid by a third party (e.g., a mutual fund company) for selling you a product. Their incentive is to recommend products that generate a commission.
- Fee-Based: A combination of fees (from you) and commissions (from products). This can create conflicts, as they may be incentivized to recommend commissioned products.

Formula for Clarity: Ask directly: Could you please provide me with your Form ADV or a written disclosure of all your potential sources of compensation?
Step 4: Conduct Your Interview and Due Diligence
Now, put it all together by interviewing 2-3 short-listed candidates.
Questions to Ask:
- Are you a Certified Financial Planner™ professional?
- Are you a fiduciary, 100% of the time?
- How do you get paid? Please explain all potential fees and commissions.
- What is your typical client profile?
- Can I see a sample financial plan?
Verification Checklist:
- Verify CFP® status on letsmakeaplan.org.
- Check for disciplinary history on FINRA BrokerCheck and the SEC’s IAPD database.
Step 5: Evaluate the Fit and the Financial Plan Itself
The final step isn’t just signing a contract. It’s about ensuring the planner’s philosophy and the proposed plan resonate with you.
What to Look for in a Sample Plan:
- Clarity and Comprehensiveness: It should be easy to understand and address all your stated goals, not just investments.
- Customization: It should feel like it was built for you, not a generic, templated document.
- Actionable Steps: A good plan provides a clear roadmap with specific actions for you to take.
- Assumptions are Clear: The plan should state its assumptions about inflation, market returns, and life expectancy.
Evaluating the Personal Fit:
- Communication Style: Do they explain things in a way you understand? Do you feel comfortable asking dumb questions?
- Philosophy Alignment: Do their investment beliefs (e.g., active vs. passive management) align with your risk tolerance?
- The Gut Check: Do you trust this person? This is a subjective but critical factor for a long-term partnership.
Common Mistake to Avoid: Rushing the decision because you feel pressured or because the planner is overly charismatic. A good advisor will give you the space and information you need to decide comfortably.
How to Use Your Findings in Your Financial Strategy
Your choice will directly impact the quality and objectivity of your financial plan.
Scenario 1: You Need Comprehensive, Objective Planning.
- Action: Prioritize interviewing Fee-Only CFP® Professionals. This combination gives you the highest standard of care (fiduciary) with a compensation model that aligns with your success. Ideal for complex situations like retirement planning, tax strategy, and estate planning.
Scenario 2: You Have a Simple, One-Off Need.
- Action: A Fee-Only CFP® who charges by the hour or project can be a cost-effective solution for a specific question, like analyzing your 401(k) options or creating a debt payoff plan.
Case Study: Sarah, a 40-year-old professional, interviewed two ‘financial planners.’ One, a non-CFP, recommended she cash out her old 401(k) to buy a high-commission annuity. The second, a CFP® fiduciary, analyzed her entire financial picture and created a plan to roll the 401(k) into a low-cost IRA and maximize her employer’s new plan match. The CFP’s advice was transparent, lower-cost, and aligned solely with Sarah’s best interest.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a Financial Planner
Pitfall 1: Choosing an advisor based solely on personality.
While rapport is important, it should not override credentials and a fiduciary obligation. Verify first, then build a relationship.
Pitfall 2: Not understanding the total cost.
Ask for an all-in cost breakdown, including fund expense ratios and advisor fees. A 1% fee can seem small but can cost you hundreds of thousands over a lifetime.
Pitfall 3: Assuming all credentials are equal.
Some credentials are more rigorous than others. CFP® is the gold standard for financial planning. Others, like ChFC, are also reputable, but many lesser-known designations can be earned in a matter of weeks.
Spotting a Great Advisor vs. a Bad One
During your interview process, keep an eye out for these clear signals.
Major Red Flags:
- Pressure to Act Immediately: Legitimate advice does not require a rushed decision.
- Unwillingness to Explain Fees: If they are vague or defensive about costs, walk away.
- Promises of Guaranteed Returns: All investing involves risk. Anyone promising specific high returns is not being truthful.
- Recommendations to Move Assets to Illiquid Products (e.g., non-traded REITs, private placements) early in the relationship. These are often high-commission and unsuitable for most investors.
- They cannot clearly articulate their fiduciary duty to you.

Positive Green Flags:
- They openly encourage you to speak with other advisors. This shows confidence in their own value proposition.
- They provide a clear, written agreement (the Advisory Agreement) that outlines services, fees, and their fiduciary duty.
- They ask as many questions as they answer, showing a genuine interest in understanding your complete picture.
- Their client references check out and speak to a long-term, trusting relationship.
- They focus on your behavior and financial plan first, and specific investments second.
- Protects Your Assets: A fiduciary is legally bound to protect your interests.
- Higher Quality Advice: CFP® professionals are required to have comprehensive knowledge.
- Peace of Mind: You gain a trusted partner, reducing financial stress and uncertainty.
- Long-Term Partnership: Establishes a relationship that can evolve with your life stages.
- Potentially Higher Upfront Cost: Fee-only advisors charge you directly, which can feel more expensive than a free advisor who is paid by commission (though often cheaper in the long run).
- May Require a Minimum Asset Level: Some fee-only CFPs require a minimum portfolio size (e.g., $100k+).
- Does Not Guarantee Performance: Even the best advisor cannot control the markets. Their value is in the plan, discipline, and strategy.
The Hidden Cost of a Non-Fiduciary Advisor
Many non-CFP planners offer free financial plans or consultations. It’s crucial to understand how they get paid and the long-term cost to you.
Scenario: A $100,000 Investment
- Fee-Only CFP® (1% AUM Fee): You pay $1,000 per year. The advisor’s incentive is to grow your portfolio, as their fee grows with it. Their advice is not influenced by product commissions.
- Commission-Based Planner: They recommend a mutual fund with a 5% front-end load and a 1% annual 12b-1 fee.
- Immediate Cost: You lose $5,000 immediately off the top ($100,000 x 5% load).
- Ongoing Cost: You pay $1,000 per year in 12b-1 fees, which often goes back to the advisor’s firm.
- The Conflict: The advisor was incentivized to recommend this fund, even if a better, no-load fund was available, because of the large upfront commission.
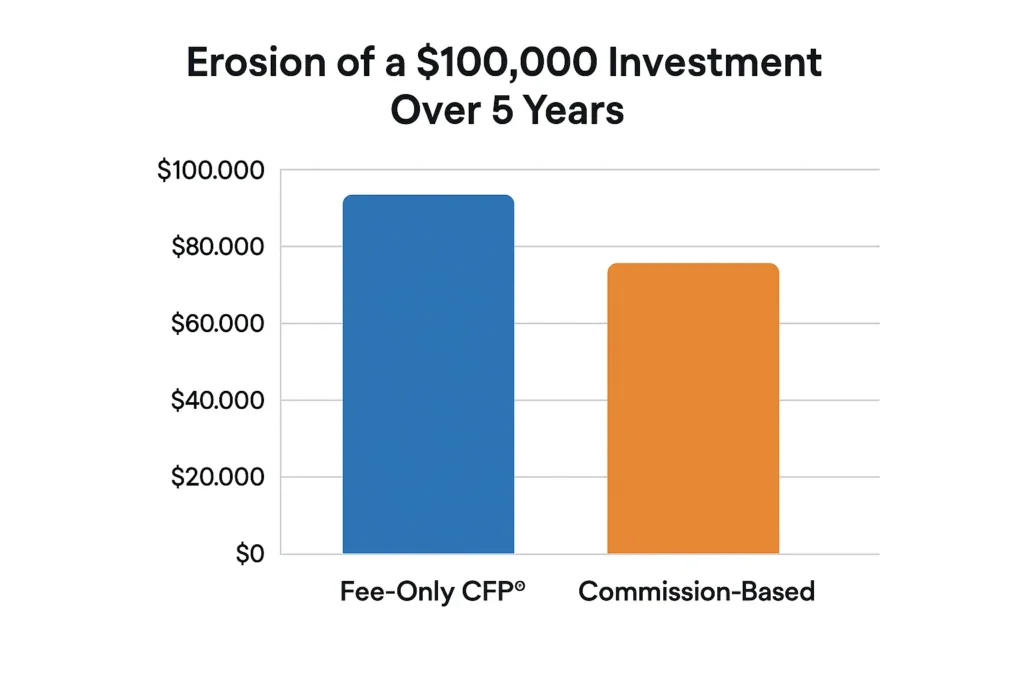
Free advice is often the most expensive advice you’ll ever receive. The costs are hidden in complex product structures that erode your wealth over time. Transparent fees from a fiduciary, while paid directly by you, are often more aligned with your success and cheaper in the long run.
Specializations and Service Models
Not all CFPs do the same thing. To add more value, consider their specializations and how they deliver services.
- Specializations:
- EA (Enrolled Agent): A tax specialist who can represent you before the IRS. Great for complex tax planning.
- AAMS (Accredited Asset Management Specialist): Focused on asset management and investment strategies.
- CRPC (Chartered Retirement Planning Counselor): Specializes in retirement income planning.
- Service Models:
- Traditional (AUM): Manages your portfolio for a percentage fee.
- Hourly/Project-Based: Pay for advice as you need it.
- Subscription/Retaiter: Pay a monthly or annual fee for ongoing access and planning.
Our Method (Vet CFP® Fiduciaries) vs Choosing a Financial Planner Based on Referral Alone
You could choose a professional using other methods, but here’s how they compare.
| Feature | Our Method (Vet CFP® Fiduciaries) | Choosing a Financial Planner Based on Referral Alone |
|---|---|---|
| Fiduciary Duty | Yes, required. | Not guaranteed; must be verified. |
| Standard of Care | Your best interest. | Suitable recommendations. |
| Conflict Management | Must be avoided or fully disclosed. | Often inherent in the compensation. |
| Verification | Rigorous, through CFP Board. | Relies on self-reporting. |
| Best For | Long-term, trusted partnerships. | Simple, transactional needs (with caution). |
Conclusion
You now possess a clear, step-by-step framework to distinguish between a salesperson with a title and a true, client-focused financial professional. The distinction between a generic Financial Planner and a Certified Financial Planner™ is profound, impacting the quality, objectivity, and cost of the advice you receive. Remember, the key is to prioritize a fiduciary duty, verify credentials, and understand how your advisor is paid.
Your fiscal future is too significant to leave to gamble. Start your search today by visiting the CFP Board’s website to find a certified professional in your area. Take control and build the future you deserve.
Related Guides You Should Read Next:
- Fee-Only vs. Fee-Based: What’s the Difference?
- How to Create a Personal Financial Plan
- Robo-Advisor vs. Human Financial Advisor: A Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
How did this post make you feel?
Thanks for your reaction!